Table of Contents
Benefits of Using a ph meter in Aquaponics Systems
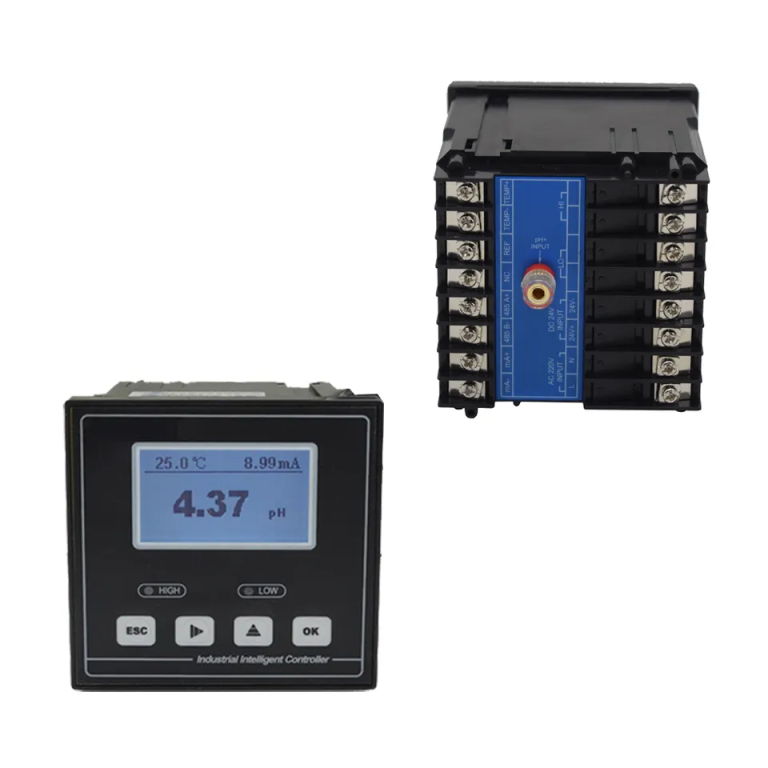
A ph meter is a valuable tool for monitoring and maintaining the pH levels in aquaponics systems. Aquaponics is a sustainable method of food production that combines aquaculture (the raising of fish) with hydroponics (the growing of plants in water). In order for the system to function properly, it is essential to keep the pH levels within a specific range. A ph meter can help achieve this by providing accurate and reliable measurements of the water’s acidity or alkalinity.
One of the primary uses of a ph meter in aquaponics is to ensure the health and well-being of the fish. Fish are sensitive to changes in pH levels, and if the water becomes too acidic or alkaline, it can have detrimental effects on their health. By regularly testing the water with a ph meter, aquaponics system owners can quickly identify any fluctuations in pH and take corrective action before it impacts the fish.
In addition to monitoring the pH levels for the fish, a ph meter is also essential for maintaining optimal conditions for plant growth. Plants in aquaponics systems rely on a balanced pH level to absorb nutrients from the water. If the pH is too high or too low, it can hinder the plants’ ability to take up essential nutrients, leading to stunted growth or even death.
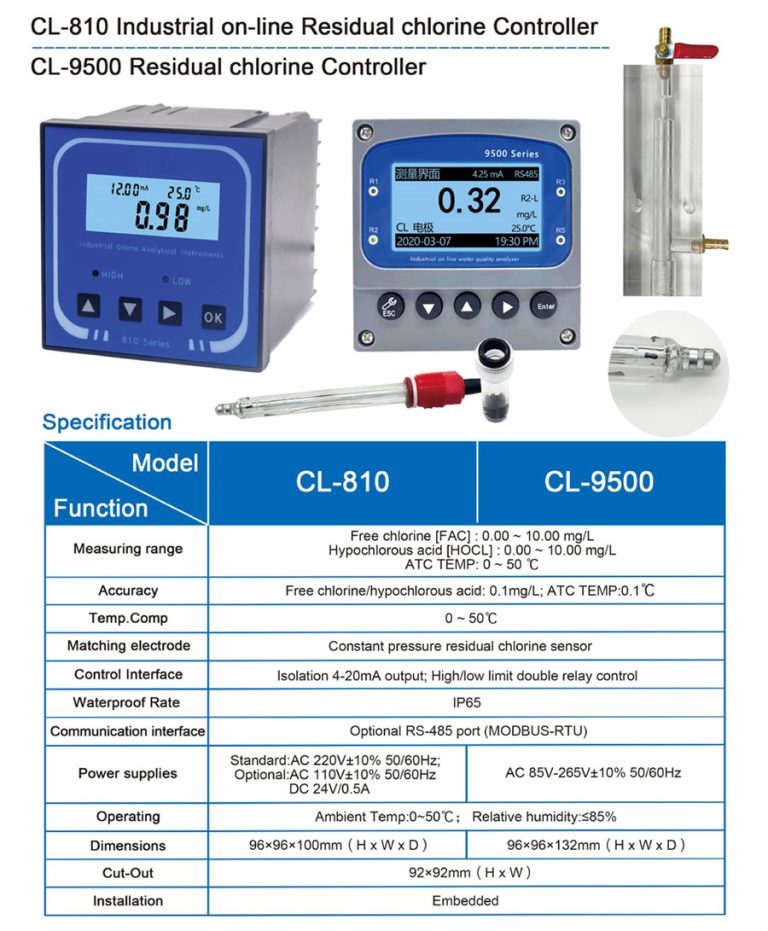
| ROS-8600 RO Program Control HMI Platform | ||
| Model | ROS-8600 Single Stage | ROS-8600 Double Stage |
| Measuring range | Source water0~2000uS/cm | Source water0~2000uS/cm |
| First level effluent 0~200uS/cm | First level effluent 0~200uS/cm | |
| secondary effluent 0~20uS/cm | secondary effluent 0~20uS/cm | |
| Pressure sensor(optional) | Membrane pre/post pressure | Primary/ secondary membrane front/rear pressure |
| ph sensor(optional) | —- | 0~14.00pH |
| Signal collection | 1.Raw water low pressure | 1.Raw water low pressure |
| 2.Primary booster pump inlet low pressure | 2.Primary booster pump inlet low pressure | |
| 3.Primary booster pump outlet high pressure | 3.Primary booster pump outlet high pressure | |
| 4.High liquid level of Level 1 tank | 4.High liquid level of Level 1 tank | |
| 5.Low liquid level of Level 1 tank | 5.Low liquid level of Level 1 tank | |
| 6.Preprocessing signal | 6.2nd booster pump outlet high pressure | |
| 7.Input standby ports x2 | 7.High liquid level of Level 2 tank | |
| 8.Low liquid level of Level 2 tank | ||
| 9.Preprocessing signal | ||
| 10.Input standby ports x2 | ||
| Output control | 1.Water inlet valve | 1.Water inlet valve |
| 2.Source water pump | 2.Source water pump | |
| 3.Primary booster pump | 3.Primary booster pump | |
| 4.Primary flush valve | 4.Primary flush valve | |
| 5.Primary dosing pump | 5.Primary dosing pump | |
| 6.Primary water over standard discharge valve | 6.Primary water over standard discharge valve | |
| 7.Alarm output node | 7.Secondary booster pump | |
| 8.Manual standby pump | 8.Secondary flush valve | |
| 9.Secondary dosing pump | 9.Secondary dosing pump | |
| Output standby port x2 | 10.Secondary water over standard discharge valve | |
| 11.Alarm output node | ||
| 12.Manual standby pump | ||
| Output standby port x2 | ||
| The main function | 1.Correction of electrode constant | 1.Correction of electrode constant |
| 2.Overrun alarm setting | 2.Overrun alarm setting | |
| 3.All working mode time can be set | 3.All working mode time can be set | |
| 4.High and low pressure flushing mode setting | 4.High and low pressure flushing mode setting | |
| 5.The low pressure pump is opened when preprocessing | 5.The low pressure pump is opened when preprocessing | |
| 6.Manual/automatic can be chosen when boot up | 6.Manual/automatic can be chosen when boot up | |
| 7.Manual debugging mode | 7.Manual debugging mode | |
| 8.Alarm if communication interruption | 8.Alarm if communication interruption | |
| 9. Urging payment settings | 9. Urging payment settings | |
| 10. Company name,website can be customized | 10. Company name,website can be customized | |
| Power supply | DC24V±10% | DC24V±10% |
| Expansion interface | 1.Reserved relay output | 1.Reserved relay output |
| 2.RS485 communication | 2.RS485 communication | |
| 3.Reserved IO port, analog module | 3.Reserved IO port, analog module | |
| 4.Mobile/computer/touch screen synchronous display | 4.Mobile/computer/touch screen synchronous display | |
| Relative humidity | ≦85% | ≤85% |
| Environment temperature | 0~50℃ | 0~50℃ |
| Touch screen size | 163x226x80mm (H x W x D) | 163x226x80mm (H x W x D) |
| Hole Size | 7 inch:215*152mm(wide*high) | 215*152mm(wide*high) |
| Controller size | 180*99(long*wide) | 180*99(long*wide) |
| Transmitter size | 92*125(long*wide) | 92*125(long*wide) |
| Installation method | Touch screen:panel embedded; Controller: plane fixed | Touch screen:panel embedded; Controller: plane fixed |
Transitional phrase: In order to ensure the success of an aquaponics system, it is crucial to use a ph meter to monitor and adjust the pH levels regularly.
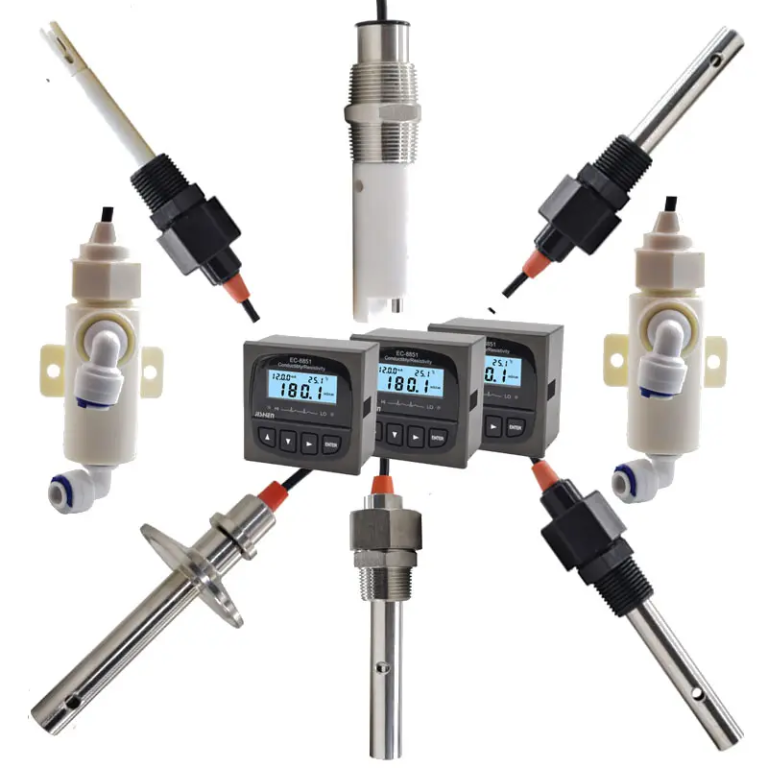
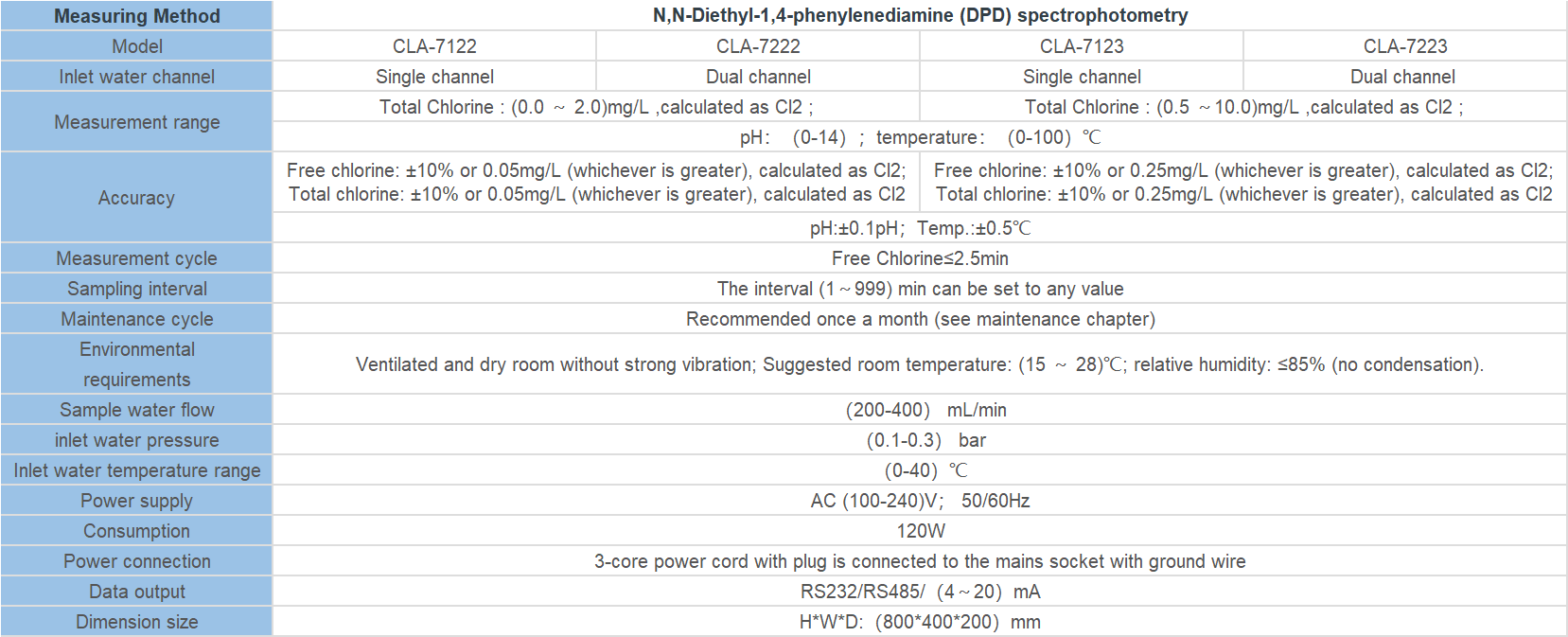
| Model | EC-510 Intelligent conductivity meter |
| Range | 0-200/2000/4000/10000uS/cm |
| 0-18.25MΩ | |
| Accuracy | 1.5%(FS) |
| Temp. Comp. | Automatic temperature compensation |
| Oper. Temp. | Normal 0~50℃; High temp 0~120℃ |
| Sensor | C=0.01/0.02/0.1/1.0/10.0cm-1 |
| Display | LCD Screen |
| Communication | 4-20mA output/2-10V/1-5V/RS485 |
| Output | High/Low limit dual relay control |
| Power | AC 220V±10% 50/60Hz or AC 110V±10% 50/60Hz or DC24V/0.5A |
| Working Environment | Ambient temperature:0~50℃ |
| Relative humidity≤85% | |
| Dimensions | 48×96×100mm(H×W×L) |
| Hole Size | 45×92mm(H×W) |
| Installation Mode | Embedded |
Another important use of a ph meter in aquaponics is to prevent nutrient deficiencies in plants. Different nutrients are available to plants at different pH levels. For example, iron is more readily available to plants in slightly acidic conditions, while phosphorus is more available in slightly alkaline conditions. By maintaining the pH within the optimal range for nutrient uptake, aquaponics system owners can ensure that their plants have access to all the essential nutrients they need for healthy growth.
Furthermore, a ph meter can also help prevent the buildup of toxic substances in the water. In aquaponics systems, fish waste is converted into nutrients for the plants by beneficial bacteria. However, if the pH levels are too high or too low, it can disrupt the balance of these bacteria, leading to the accumulation of harmful substances such as ammonia or nitrites. By regularly testing the pH with a meter, aquaponics system owners can catch any imbalances early on and take steps to correct them before they become a problem.
Transitional phrase: By using a ph meter to monitor the water quality in an aquaponics system, owners can ensure that both the fish and plants thrive in a healthy environment.
In conclusion, a ph meter is an essential tool for maintaining the health and productivity of aquaponics systems. By monitoring the pH levels regularly, aquaponics system owners can ensure that the fish and plants have the optimal conditions they need to thrive. Whether it’s preventing nutrient deficiencies, avoiding toxic buildup, or simply keeping the system in balance, a ph meter is a valuable investment for anyone looking to succeed in aquaponics.
Importance of ph meter in Brewing Beer
A ph meter is a crucial tool in the brewing process, as it helps brewers monitor and control the acidity of their beer. The pH level of beer plays a significant role in determining its flavor, stability, and overall quality. In this article, we will discuss two important uses of a ph meter in brewing beer.
First and foremost, a ph meter is used to measure the acidity of the mash during the brewing process. The mash is a mixture of crushed grains and hot water that is used to extract sugars and other fermentable compounds from the grains. The pH of the mash is critical because it affects the activity of enzymes that break down starches into sugars. If the pH is too high or too low, the enzymes may not function properly, leading to a decrease in sugar extraction and ultimately affecting the flavor and alcohol content of the beer.
By using a ph meter to monitor the acidity of the mash, brewers can make adjustments to ensure that the pH remains within the optimal range for enzyme activity. This may involve adding acids or alkaline substances to the mash to bring the pH into the desired range. By maintaining the correct pH level, brewers can maximize sugar extraction, improve fermentation efficiency, and ultimately produce a beer with the desired flavor profile.
Another important use of a ph meter in brewing beer is during the fermentation process. Yeast, the microorganism responsible for converting sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide, is sensitive to changes in pH. If the pH of the fermentation wort is too high or too low, it can inhibit yeast activity and lead to stalled fermentation or off-flavors in the finished beer.
By regularly measuring the pH of the fermentation wort with a ph meter, brewers can ensure that the environment is conducive to yeast activity. If the pH begins to drift outside of the optimal range, brewers can make adjustments by adding acids or alkaline substances to bring the pH back into balance. This proactive approach helps to maintain a healthy fermentation process, resulting in a beer with consistent flavor, aroma, and alcohol content.
In conclusion, a ph meter is an essential tool for brewers looking to produce high-quality beer. By monitoring and controlling the acidity of the mash and fermentation wort, brewers can optimize sugar extraction, fermentation efficiency, and overall beer quality. Whether you are a homebrewer or a professional brewer, investing in a ph meter is a wise decision that will help you achieve the desired flavor profile and consistency in your beer.