Understanding the Role of Solenoid Valves in control valve Technology
Understanding the role of solenoid valves in control valve technology is crucial in various industries, particularly those that rely heavily on fluid control systems. These include sectors such as manufacturing, oil and gas, water treatment, and many others. Solenoid valves, as integral components of control valve technology, play a pivotal role in managing the flow of liquids and gases in these systems.
A solenoid valve is an electromechanically operated device used to control the flow of fluids or gases. It operates by using an electric current to generate a magnetic field, which then moves a plunger inside the valve, opening or closing it. This mechanism allows for precise control over the flow rate, direction, and timing of the fluid or gas passing through the system.
One of the primary advantages of solenoid valves in control valve technology is their ability to offer rapid and reliable switching operations. This is particularly beneficial in applications where quick response times are essential. For instance, in a manufacturing process where a sudden stop in the flow of a liquid or gas could result in equipment damage or safety hazards, the quick action of a solenoid valve can prevent such incidents.
Moreover, solenoid valves are known for their high degree of accuracy. They can maintain precise control over the flow of fluids or gases, even under varying pressure conditions. This precision is crucial in applications where maintaining a specific flow rate is necessary for optimal system performance. For example, in a water treatment plant, the accurate control of chemical dosing is vital to ensure the water’s safety and quality.
Another significant advantage of solenoid valves is their versatility. They come in various types and sizes, each designed to meet specific application requirements. Some solenoid valves are designed for high-pressure applications, while others are suitable for low-pressure systems. There are also solenoid valves designed for use with different types of fluids or gases, including corrosive or high-temperature substances. This wide range of options allows for the customization of control valve systems to meet the unique needs of different industries.
| Model | Central tube | Drain | Brine tank connector | Base | Power supply parameters | Maximum power | Pressure parameters | Operating temperature |
| 5600 | 0.8125″/1.050″ O.D. | 1/2″NPTF | 1600-3/8″ | 2-1/2″-8NPSM | 24v,110v,220v-50Hz,60Hz | 3W | 2.1MPa | 1℃-43℃ |
| 0.14-0.84MPa | ||||||||
| 5600SXT | 0.8125″/1.050″ O.D. | 1/2″NPTF | 1600-3/8″ | 2-1/2″-8NPSM | 24v,110v,220v-50Hz,60Hz | 8.4W | 2.1MPa | 1℃-43℃ |
| 0.14-0.84MPa | ||||||||
| 2510 | 1.05″ (1″)O.D. | 1/2″O.D. | 1600-3/8″ | 2-1/2″-8NPSM | 24v,110v,220v-50Hz,60Hz | 72W | 2.1MPa | 1℃-43℃ |
| 1650-3/8″ | 0.14-0.84MPa | |||||||
| 2700 | 1.05″ O.D. | 3/4″NPTF | 3/8″ & 1/2″ | 2-1/2″-8NPSM | 24V,110V,220V-50Hz,60Hz | 74W | 2.1MPa | 1℃-43℃ |
| 0.14-0.84MPa | ||||||||
| 2850 | 1.9″(1.5″)O.D. | 1″NPTM | 3/8″&1/2″ | 4″-8UN | 24v,110v,220v-50Hz,60Hz | 72W | 2.1MPa | 1℃-43℃ |
| 0.14-0.84MPa | ||||||||
| 2900 | 1.9″(1.5″)O.D. | 3/4″NPTM | 3/8″&1/2″ | 4″-8UN | 24v,110v,220v-50Hz,60Hz | 143W | 2.1MPa | 1℃-43℃ |
| 0.14-0.84MPa | ||||||||
| 3150 | 2.375″(2″) O.D. | 2″NPTF | 1″NPTM | 4″-8UN | 24v,110v,220v-50Hz,60Hz | 87W | 2.1MPa | 1℃-43℃ |
| 0.14-0.84MPa | ||||||||
| 3900 | 3.5″(3″) O.D. | 2″NPTF | 1″NPTM | 6″-8UN | 24v,110v,220v-50Hz,60Hz | 171W | 2.1MPa | 1℃-43℃ |
| 0.14-0.84MPa | ||||||||
| 9000 | 1.05″ O.D. | 1/2″NPT | 1600-3/8″ | 2-1/2″-8NPSM | 24v,110v,220v-50Hz,60Hz | 8.9W | 2.1MPa | 1℃-43℃ |
| 0.14-0.84MPa | ||||||||
| 9100 | 1.05″ O.D. | 1/2″NPT | 1600-3/8″ | 2-1/2″-8NPSM | 24v,110v,220v-50Hz,60Hz | 8.9W | 2.1MPa | 1℃-43℃ |
| 0.14-0.84MPa | ||||||||
| 9500 | 1.9″(1.5″) O.D. | 1″NPTF | 3/8″& 1/2″ | 4″-8UN | 24v,110v,220v-50Hz,60Hz | 8.9W | 2.1MPa | 1℃-43℃ |
| 0.14-0.84MPa |
Furthermore, solenoid valves are relatively easy to install and maintain. They can be integrated into existing control valve systems with minimal modifications. Their simple design also makes them less prone to mechanical failures, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacements.

However, despite their many advantages, solenoid valves are not without their limitations. They are typically not suitable for applications that require continuous operation or those that involve high flow rates. They can also be affected by electrical interference, which can impact their performance.
| Model: Automatic Softener Valve | ASE2 -LCD/LED | |
| Refilling type | refill before regeneration | refill after regeneration |
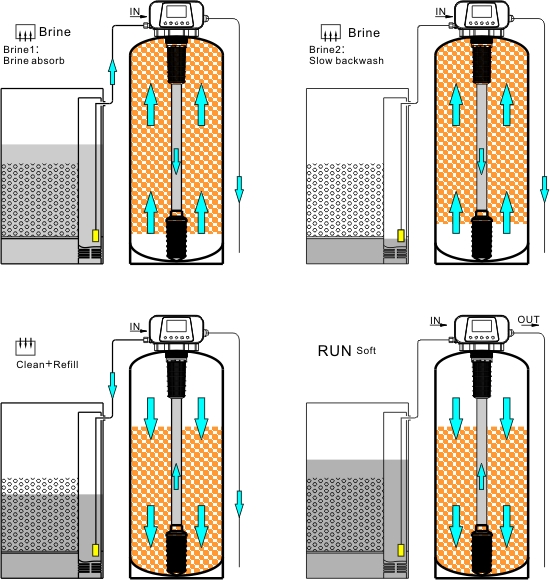
| Working Position | Service->Refill the softener water->Service->Back Wash->Upflow Brine and slow rinse->Fast rinse->Service | Service->Back Wash->Upflow Brine and slow rinse-> Fast rinse-> Refill the softener water->Service |
| Automatic type | Automatic type | |
| Meter Delay | Meter Delay | |
| Regeneration mode | Intelligent Meter Delay | Meter immediate |
| Timer by day : 0-99 days | Intelligent Meter Delay | |
| Timer by hours: 0-99 hours | Intelligent Meter Immediate | |
| Timer by day : 0-99 days | ||
| Timer by hours: 0-99 hours | ||
| Inlet | 1/2” 3/4” 1” | |
| Outlet | 1/2” 3/4” 1” | |
| Drain | 1/2” | |
| Base | 2-1/2” | |
| Riser pipe | 1.05” OD | |
| Water Capacity | 2m3/h | |
| Working Pressure | 0.15-0.6Mpa | |
| Working Temperature | 5-50°C | |
| Power Supply | AC100-240 / 50-60Hz / DC12V-1.5A | |
In conclusion, solenoid valves play a critical role in control valve technology. Their ability to provide rapid, reliable, and precise control over the flow of fluids or gases makes them an invaluable tool in various industries. While they do have some limitations, their benefits often outweigh these drawbacks, making them a popular choice for many fluid control applications. Understanding the role and functionality of solenoid valves can help in selecting the right type of valve for a specific application, ultimately leading to improved system performance and efficiency.






