Understanding the Importance of Water Flow Transducers in Industrial Applications
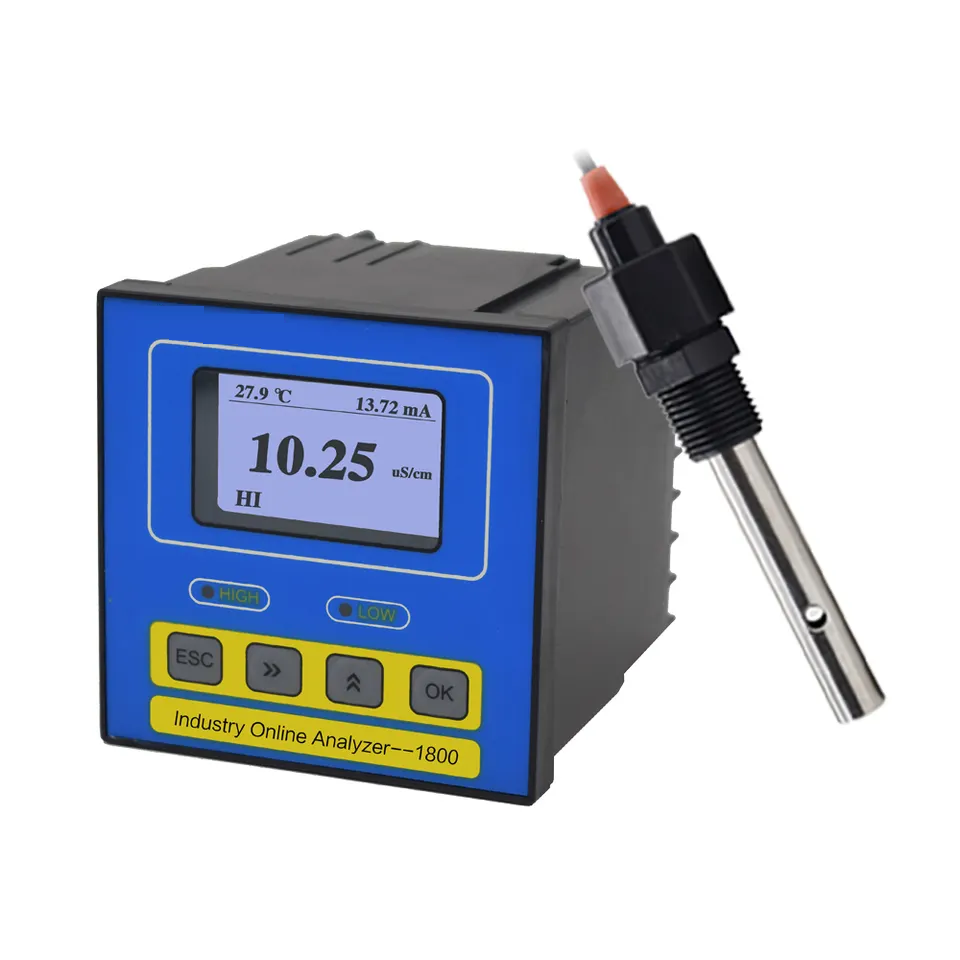
Water flow transducers play a crucial role in various industrial applications, providing accurate measurements of water flow rates. These devices are essential for monitoring and controlling water flow in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, agriculture, and wastewater treatment. Understanding the importance of water flow transducers is key to ensuring efficient and reliable operations in these industries.
One of the primary functions of water flow transducers is to measure the rate at which water is flowing through a system. This information is vital for maintaining optimal performance and efficiency in industrial processes. By accurately measuring water flow rates, operators can make informed decisions about how to adjust flow rates to meet production requirements or prevent equipment damage.
Water flow transducers are also essential for detecting leaks or other issues in water systems. By continuously monitoring flow rates, these devices can alert operators to any sudden changes that may indicate a problem. Early detection of leaks can help prevent costly damage to equipment and infrastructure, as well as minimize water waste.
In addition to monitoring flow rates, water flow transducers can also be used to control the flow of water in a system. By integrating these devices with control systems, operators can adjust flow rates automatically to maintain desired levels. This level of automation can help improve efficiency and reduce the need for manual intervention, saving time and labor costs.
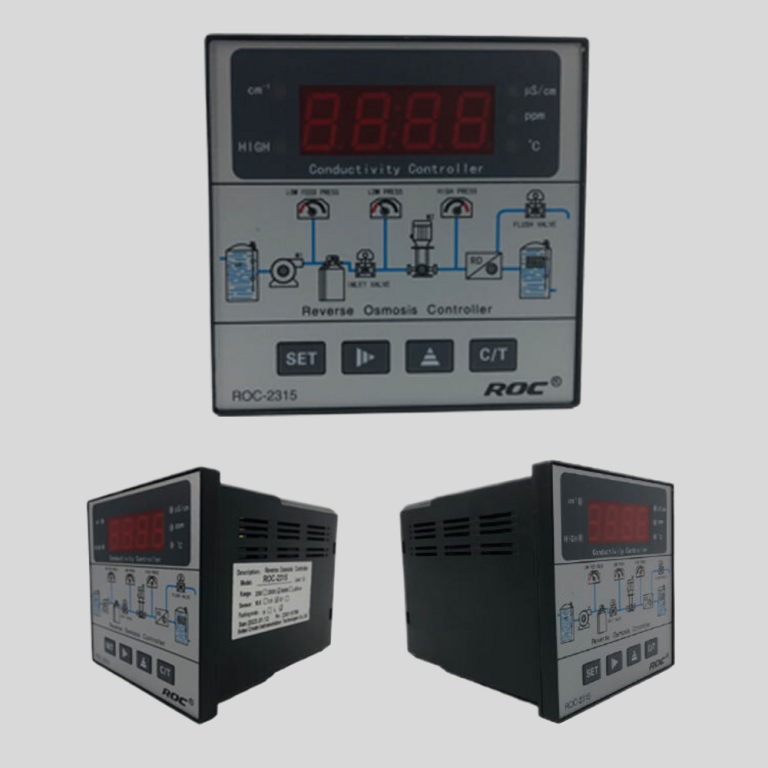
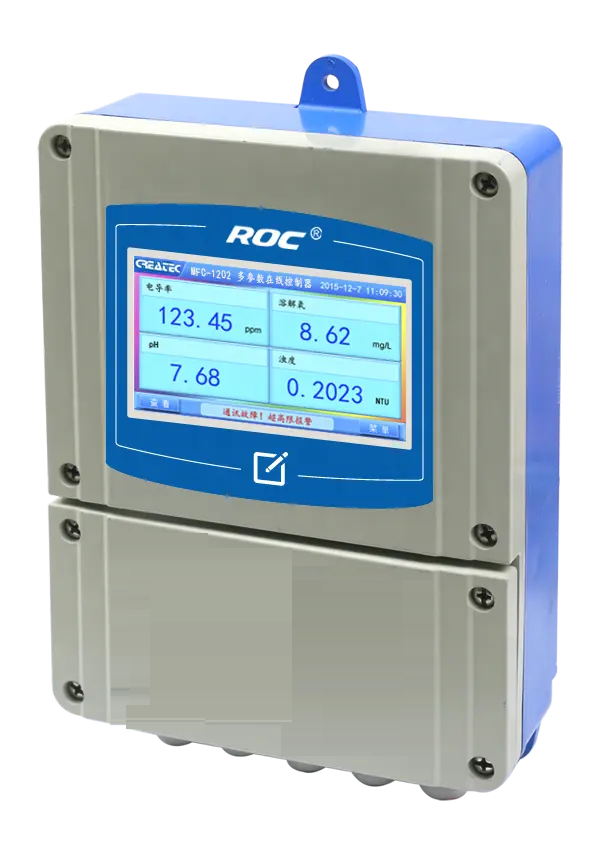
| ROS-8600 RO Program Control HMI Platform | ||
| Model | ROS-8600 Single Stage | ROS-8600 Double Stage |
| Measuring range | Source water0~2000uS/cm | Source water0~2000uS/cm |
| \u3000 | First level effluent 0~200uS/cm | First level effluent 0~200uS/cm |
| \u3000 | secondary effluent 0~20uS/cm | secondary effluent 0~20uS/cm |
| Pressure sensor(optional) | Membrane pre/post pressure | Primary/ secondary membrane front/rear pressure |
| ph sensor(optional) | —- | 0~14.00pH |
| Signal collection | 1.Raw water low pressure | 1.Raw water low pressure |
| \u3000 | 2.Primary booster pump inlet low pressure | 2.Primary booster pump inlet low pressure |
| \u3000 | 3.Primary booster pump outlet high pressure | 3.Primary booster pump outlet high pressure |
| \u3000 | 4.High liquid level of Level 1 tank | 4.High liquid level of Level 1 tank |
| \u3000 | 5.Low liquid level of Level 1 tank | 5.Low liquid level of Level 1 tank |
| \u3000 | 6.Preprocessing signal\u00a0 | 6.2nd booster pump outlet high pressure |
| \u3000 | 7.Input standby ports x2 | 7.High liquid level of Level 2 tank |
| \u3000 | \u3000 | 8.Low liquid level of Level 2 tank |
| \u3000 | \u3000 | 9.Preprocessing signal |
| \u3000 | \u3000 | 10.Input standby ports x2 |
| Output control | 1.Water inlet valve | 1.Water inlet valve |
| \u3000 | 2.Source water pump | 2.Source water pump |
| \u3000 | 3.Primary booster pump | 3.Primary booster pump |
| \u3000 | 4.Primary flush valve | 4.Primary flush valve |
| \u3000 | 5.Primary dosing pump | 5.Primary dosing pump |
| \u3000 | 6.Primary water over standard discharge valve | 6.Primary water over standard discharge valve |
| \u3000 | 7.Alarm output node | 7.Secondary booster pump |
| \u3000 | 8.Manual standby pump | 8.Secondary flush valve |
| \u3000 | 9.Secondary dosing pump | 9.Secondary dosing pump |
| \u3000 | Output standby port x2 | 10.Secondary water over standard discharge valve |
| \u3000 | \u3000 | 11.Alarm output node |
| \u3000 | \u3000 | 12.Manual standby pump |
| \u3000 | \u3000 | Output standby port x2 |
| The main function | 1.Correction of electrode constant | 1.Correction of electrode constant |
| \u3000 | 2.Overrun alarm setting | 2.Overrun alarm setting |
| \u3000 | 3.All working mode time can be set | 3.All working mode time can be set |
| \u3000 | 4.High and low pressure flushing mode setting | 4.High and low pressure flushing mode setting |
| \u3000 | 5.The low pressure pump is opened when preprocessing | 5.The low pressure pump is opened when preprocessing |
| \u3000 | 6.Manual/automatic can be chosen when boot up | 6.Manual/automatic can be chosen when boot up |
| \u3000 | 7.Manual debugging mode | 7.Manual debugging mode |
| \u3000 | 8.Alarm if communication interruption | 8.Alarm if communication interruption |
| \u3000 | 9. Urging payment settings | 9. Urging payment settings |
| \u3000 | 10. Company name,website can be customized | 10. Company name,website can be customized |
| Power supply | DC24V\u00b110% | DC24V\u00b110% |
| Expansion interface | 1.Reserved relay output | 1.Reserved relay output |
| \u3000 | 2.RS485 communication | 2.RS485 communication |
| \u3000 | 3.Reserved IO port, analog module | 3.Reserved IO port, analog module |
| \u3000 | 4.Mobile/computer/touch screen synchronous display\u00a0 | 4.Mobile/computer/touch screen synchronous display\u00a0 |
| Relative humidity | \u226685% | \u226485% |
| Environment temperature | 0~50\u2103 | 0~50\u2103 |
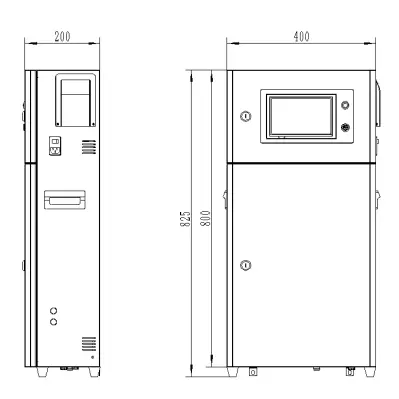
| Touch screen size | 163x226x80mm (H x W x D) | 163x226x80mm (H x W x D) |
| Hole Size | 7 inch:215*152mm(wide*high) | 215*152mm(wide*high) |
| Controller size | 180*99(long*wide) | 180*99(long*wide) |
| Transmitter size | 92*125(long*wide) | 92*125(long*wide) |
| Installation method | Touch screen:panel embedded; Controller: plane fixed | Touch screen:panel embedded; Controller: plane fixed |
Water flow transducers come in a variety of types and designs, each suited to different applications and environments. Some transducers use mechanical components, such as turbines or paddlewheels, to measure flow rates, while others rely on ultrasonic or electromagnetic technology. The choice of transducer depends on factors such as the type of water being measured, the flow rate range, and the operating conditions.
Proper installation and calibration of water flow transducers are essential for accurate and reliable measurements. Transducers should be installed in a location that allows for a consistent flow profile and minimal turbulence. Regular calibration and maintenance are also necessary to ensure that transducers continue to provide accurate readings over time.