“Precision and Control: Unleash the Perfect Blend with Mixing Valves.”
Understanding the Functionality of Mixing Valves
Understanding the Functionality of Mixing Valves
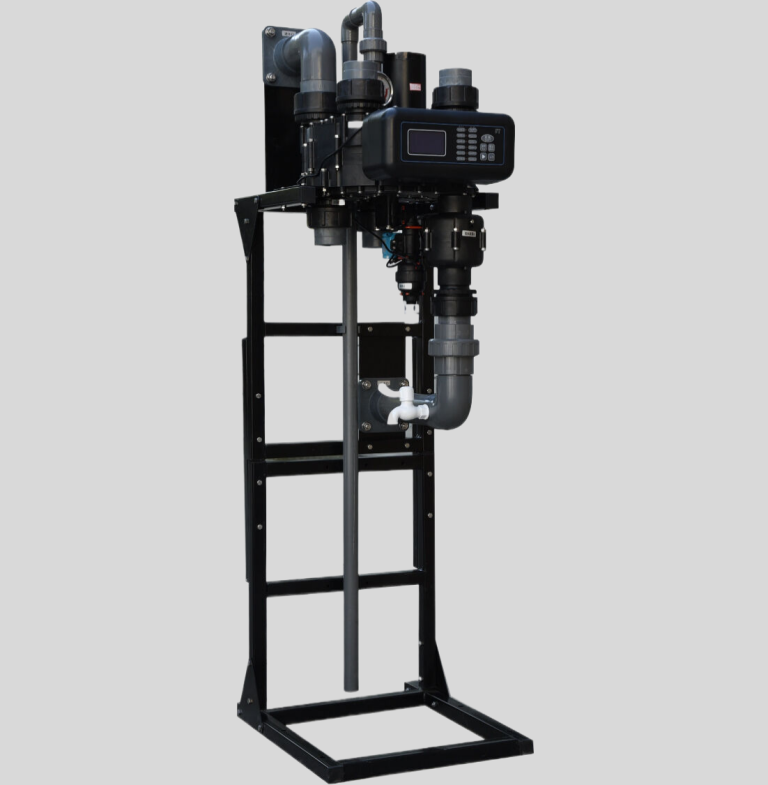
| Model | Central tube | Drain | Brine tank connector | Base | Power supply parameters | Maximum power | Pressure parameters | Operating temperature |
| 9000 | 1.05″ O.D. | 1/2″NPT | 1600-3/8″ | 2-1/2″-8NPSM | 24v,110v,220v-50Hz,60Hz | 8.9W | 2.1MPa | 1℃-43℃ |
| 0.14-0.84MPa |
Mixing valves are an essential component in various plumbing systems, providing a crucial function that ensures the delivery of safe and comfortable water temperatures. These valves are commonly found in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, and understanding how they work is essential for anyone involved in plumbing or building maintenance.
At its core, a mixing valve is designed to regulate the temperature of water by blending hot and cold water streams. This process is crucial in applications where precise control over water temperature is necessary, such as in showers, bathtubs, and sinks. By adjusting the ratio of hot and cold water, mixing valves allow users to achieve their desired temperature, preventing scalding or discomfort.
The basic mechanism of a mixing valve involves the use of a thermostatic element, which responds to changes in water temperature. This element is typically made of a wax-filled cylinder or a bimetallic strip that expands or contracts based on the temperature of the water flowing through it. As the thermostatic element reacts to temperature changes, it triggers the valve to adjust the flow of hot and cold water accordingly.
When the water temperature is too hot, the thermostatic element expands, causing the valve to reduce the flow of hot water and increase the flow of cold water. Conversely, when the water temperature is too cold, the thermostatic element contracts, allowing more hot water to flow while reducing the cold water flow. This continuous adjustment ensures that the water temperature remains within a safe and comfortable range.
To achieve this temperature regulation, mixing valves are equipped with internal mechanisms that control the flow of hot and cold water. These mechanisms can vary depending on the specific type of mixing valve, but they generally involve the use of diaphragms, pistons, or other movable components. These components work together to adjust the flow rates of hot and cold water, maintaining the desired temperature.
In addition to temperature regulation, mixing valves also play a crucial role in preventing scalding accidents. Many mixing valves are equipped with a temperature limit stop, which allows users to set a maximum temperature to prevent water from becoming dangerously hot. This feature is particularly important in settings where vulnerable individuals, such as children or the elderly, may be using the water supply.
Furthermore, mixing valves can also help conserve energy and water. By precisely controlling the temperature, these valves reduce the need for excessive hot water, resulting in energy savings. Additionally, they can prevent wastage by maintaining a consistent temperature, eliminating the need for users to continuously adjust the hot and cold water taps.
In conclusion, understanding the functionality of mixing valves is crucial for anyone involved in plumbing or building maintenance. These valves play a vital role in regulating water temperature, preventing scalding accidents, and conserving energy and water. By blending hot and cold water streams, mixing valves ensure the delivery of safe and comfortable water temperatures in various applications. Whether in residential, commercial, or industrial settings, the proper functioning of mixing valves is essential for the well-being and comfort of users.