Table of Contents
Benefits of Zinc Conductivity in Electrical Applications
Zinc is a versatile metal that has a wide range of applications in various industries. One of the key properties of zinc that makes it so valuable in electrical applications is its high conductivity. Conductivity refers to the ability of a material to conduct electricity, and zinc is known for its excellent conductivity properties.
When it comes to electrical applications, having a material with high conductivity is crucial. This is because materials with high conductivity allow electricity to flow through them with minimal resistance. This means that less energy is lost as heat during the transmission of electricity, making the system more efficient.
Zinc’s high conductivity makes it an ideal material for use in electrical wiring and components. In wiring, zinc is often used as a coating on copper wires to improve their conductivity. This helps to reduce energy loss and improve the overall efficiency of the electrical system. Additionally, zinc is also used in the production of electrical components such as connectors and terminals, where its conductivity properties are highly beneficial.
Another benefit of zinc conductivity in electrical applications is its corrosion resistance. Zinc is a highly durable metal that is resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for use in outdoor or harsh environments. This is particularly important in electrical applications where exposure to moisture or other corrosive elements can degrade the performance of the system. By using zinc-coated components, manufacturers can ensure that their electrical systems remain reliable and efficient over time.
In addition to its conductivity and corrosion resistance, zinc also has the advantage of being a relatively inexpensive material. This makes it a cost-effective choice for manufacturers looking to produce high-quality electrical components without breaking the bank. By using zinc in their products, manufacturers can achieve the desired level of conductivity and durability at a fraction of the cost of other materials.
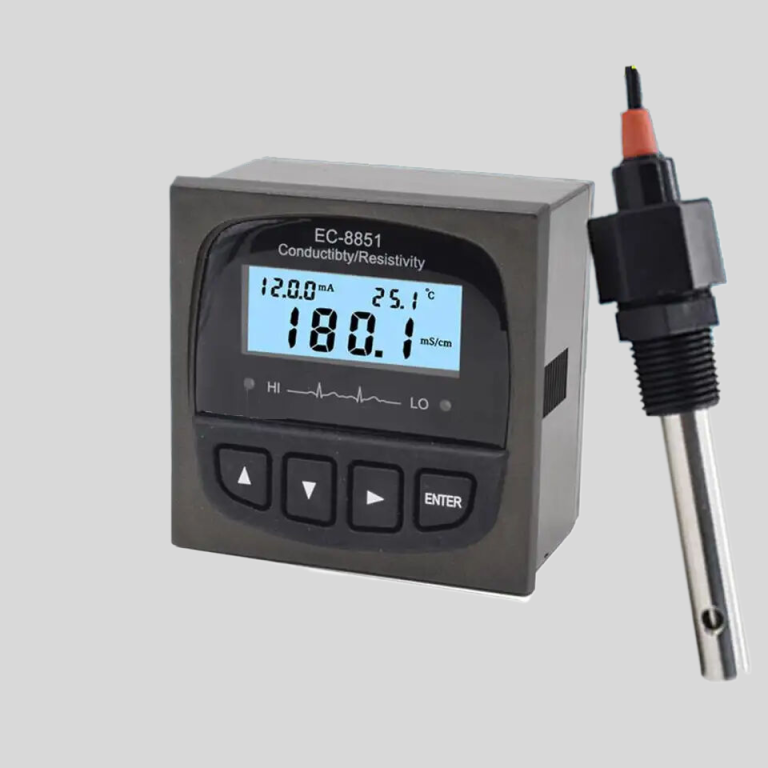
| Model | pH/ORP-8500A pH/ORP Online Meter |
| Range | pH:0.00~14.00 ; ORP:(-1999~+1999)mV; Temp.:(0.0~100.0)°C (Temp.Compensation: NTC10K) |
| Resolution | pH:0.01 ; ORP: 1mV; Temp.:0.1°C |
| Accuracy | pH:+/-0.1 ; ORP: +/-5mV(electronic unit); Temp.: +/-0.5°C |
| Temp. compensation | NTC10K Temperature compensation |
| Medium Temp. | (0~80)°C |
| Analog output | Double channels isolated; transportable(4~20)mA, instruments/ transmitter mode |
| Control Output | Triple channels semiconductor photoelectric switch, load current: AC/DC 30V, 50mA(max) |
| Communication port | RS485,Modbus RTU protocol |
| Working Environment | Temp.(0~80)℃; relative humidity <95%RH (non-condensing) |
| Storage Environment | Temp.(-20~60)℃;Relative Humidity ≤85%RH (none condensation) |
| Power Supply | DC 24V |
| Power consumption | <3W |
| Protection level | IP65 (with back cover) |
| Dimension | 96mmx96mmx94mm(HxWxD) |
| Hole Size | 91mmx91mm(HxW) |
Furthermore, zinc is a sustainable material that is widely available and easily recyclable. This makes it an environmentally friendly choice for manufacturers looking to reduce their carbon footprint and minimize waste. By using zinc in their electrical applications, manufacturers can contribute to a more sustainable future while still meeting their performance requirements.
How Zinc Conductivity Affects the Performance of Electronic Devices
Zinc is a versatile metal that is widely used in various industries, including electronics. One of the key properties of zinc that makes it so valuable in electronic devices is its conductivity. Conductivity refers to the ability of a material to conduct electricity, and zinc is known for its high electrical conductivity.
When it comes to electronic devices, conductivity plays a crucial role in determining their performance. The higher the conductivity of a material, the better it is at conducting electricity, which is essential for the proper functioning of electronic components. Zinc’s high conductivity makes it an ideal choice for use in electronic devices, as it allows for efficient flow of electricity through the device.

In electronic devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets, zinc is often used in various components, such as circuit boards, connectors, and batteries. These components rely on zinc’s conductivity to ensure that electricity can flow smoothly and efficiently through the device. Without high conductivity, electronic devices would not be able to function properly, leading to poor performance and potential malfunctions.
One of the key benefits of using zinc in electronic devices is its low resistance to electricity. Resistance refers to the opposition that a material offers to the flow of electricity, and materials with high resistance can impede the flow of electricity through a device. Zinc’s low resistance allows for efficient flow of electricity, which is essential for the proper functioning of electronic devices.
In addition to its high conductivity and low resistance, zinc is also a highly durable and corrosion-resistant metal. This makes it an ideal choice for use in electronic devices, as it can withstand the rigors of daily use and exposure to various environmental factors. Zinc’s durability ensures that electronic devices can continue to function properly over an extended period, without the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
| Model | EC-1800 online conductivity controller |
| Range | 0-2000/4000uS/cm 0-20/200mS/cm |
| 0-1000/2000PPM | |
| Accuracy | 1.5%, 2%, 3%(FS) |
| Temp. Comp. | Automatic temperature compensation based on 25℃ |
| Oper. Temp. | Normal 0~50℃; High temp 0~120℃ |
| Sensor | C=0.1/1.0/10.0cm-1 |
| Display | 128*64 LCD Screen |
| Communication | 4-20mA output/2-10V/1-5V/RS485 |
| Output | High/Low limit dual relay control |
| Power | AC 220V±10% 50/60Hz or AC 110V±10% 50/60Hz or DC24V/0.5A |
| Working Environment | Ambient temperature:0~50℃ |
| Relative humidity≤85% | |
| Dimensions | 96×96×100mm(H×W×L) |
| Hole Size | 92×92mm(H×W) |
| Installation Mode | Embedded |
Furthermore, zinc is a cost-effective material that is readily available in abundance. This makes it a practical choice for use in electronic devices, as it helps to keep production costs down while still ensuring high performance. Manufacturers can rely on zinc to provide the conductivity and durability needed for electronic devices, without breaking the bank.
Overall, zinc conductivity plays a crucial role in determining the performance of electronic devices. Its high conductivity, low resistance, durability, and cost-effectiveness make it an ideal choice for use in various components of electronic devices. Without zinc’s conductivity, electronic devices would not be able to function properly, leading to poor performance and potential malfunctions. As technology continues to advance, zinc will likely continue to play a key role in the development of high-performance electronic devices.







