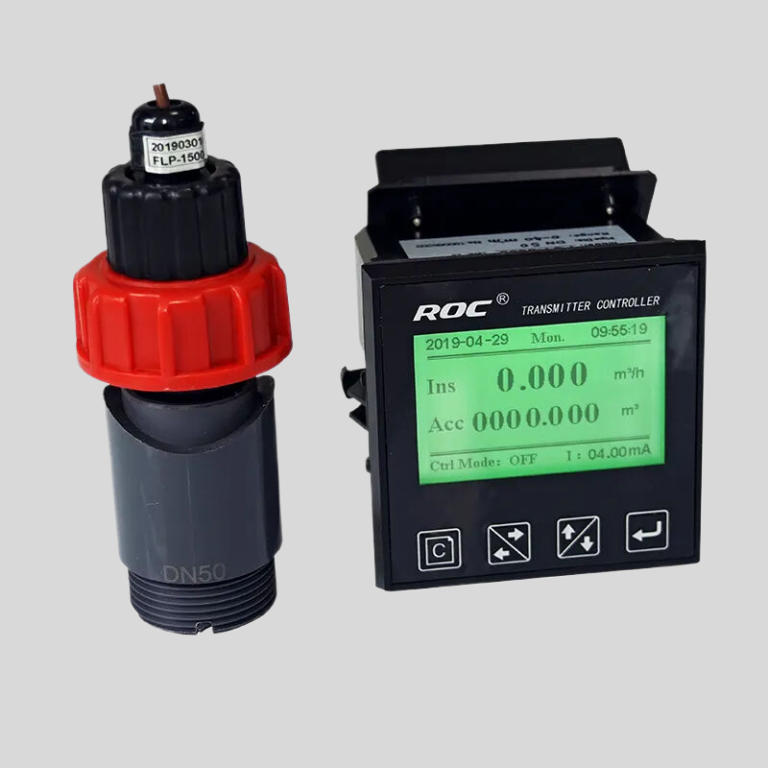
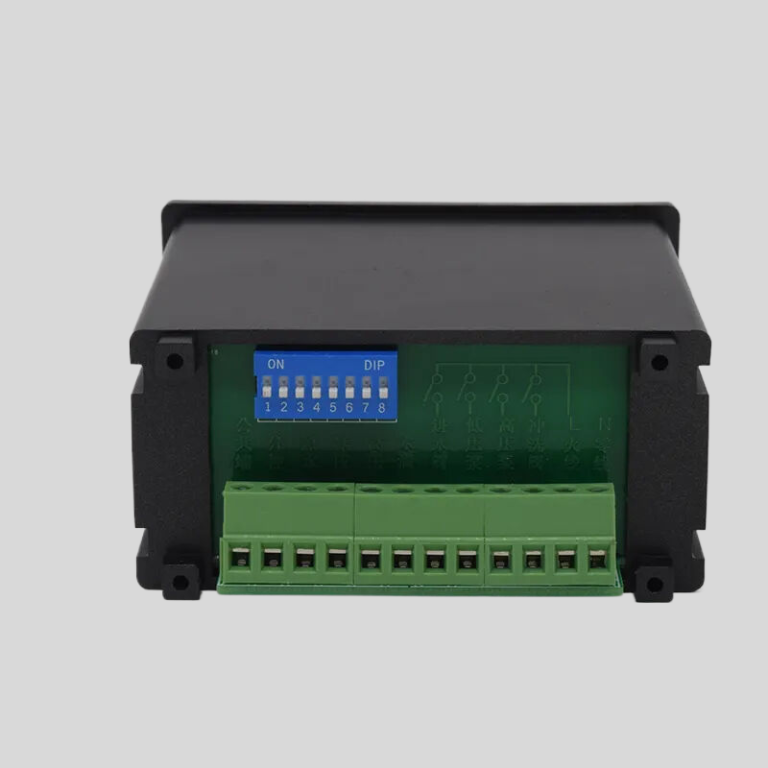
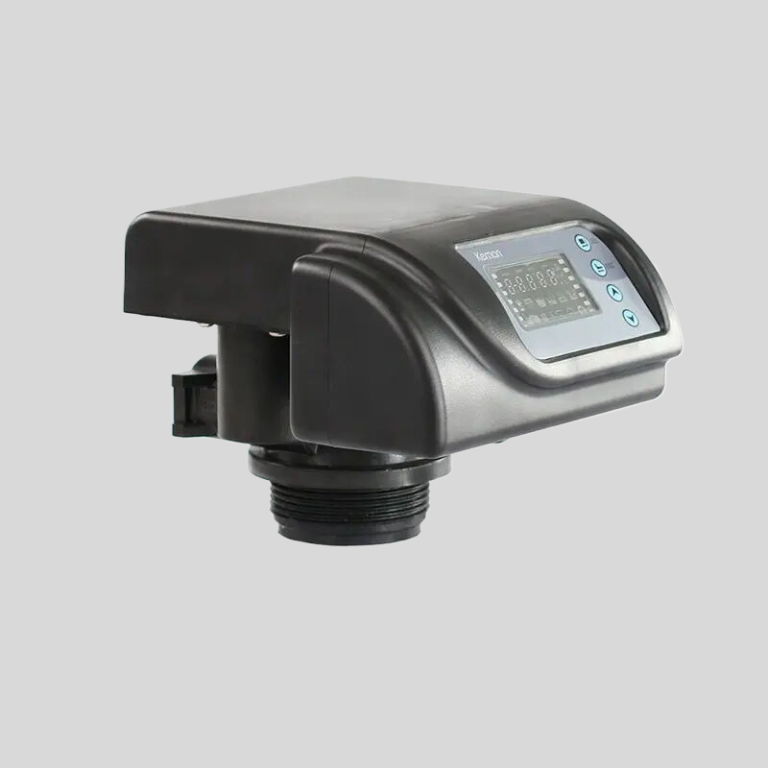
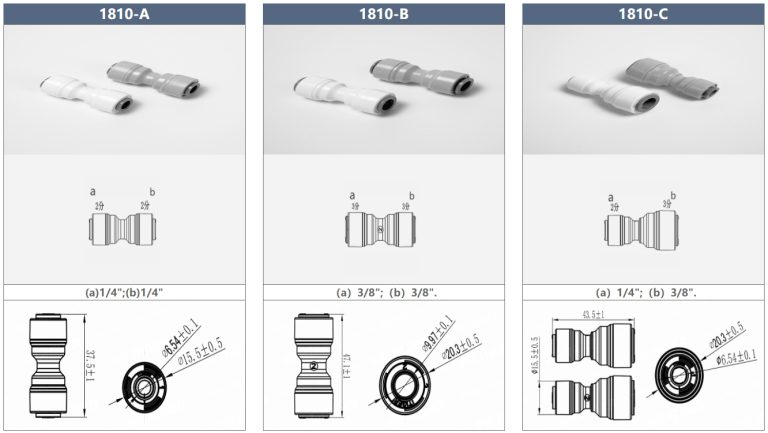
Joints : Indispensables pour une étanchéité parfaite.
Introduction aux joints : ce que vous devez savoir
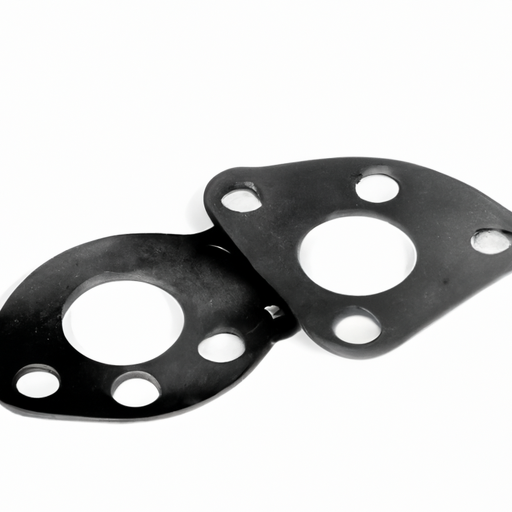

Les joints sont un composant essentiel dans diverses industries, jouant un rôle crucial pour assurer le bon fonctionnement des machines et des équipements. Ces dispositifs petits mais puissants sont utilisés pour créer un joint entre deux ou plusieurs surfaces, empêchant ainsi les fuites de fluides ou de gaz. Dans cet article, nous plongerons dans le monde des joints, en explorant leurs différents types, matériaux et applications.Les joints sont disponibles dans une large gamme de formes, de tailles et de matériaux, chacun étant conçu pour répondre à des exigences spécifiques. Les types de joints les plus courants comprennent les joints en feuille, les joints enroulés en spirale, les joints annulaires et les joints solides. Les joints en feuille sont fabriqués à partir de matériaux tels que le caoutchouc, le liège ou le graphite et sont connus pour leur flexibilité et leur facilité d’installation. Les joints enroulés en spirale, quant à eux, sont constitués d’un enroulement métallique et d’un matériau de remplissage, offrant une excellente résistance aux températures et pressions élevées. Les joints annulaires sont généralement utilisés dans les raccords à brides, tandis que les joints solides sont fabriqués à partir d’une seule pièce de matériau et sont souvent utilisés dans les applications basse pression. Modèle : Valve de filtre manuelle
Modèle : Valve de filtre manuelle
| MF2 | MF2-H | MF4 | MF4-B | MF10 | Position de travail |
| Filtre – | Mode régénération | ||||
| Manuel | Entrée | ||||
| Prise | 3/4” | 3/4” | 1” | 1” | 2” |
| Vidange | 3/4” | 3/4” | 1” | 1” | 2” |
| Base | 3/4” | 3/4” | 1” | 1” | 2” |
| Tuyau montant | 2-1/2” | 2-1/2” | 2-1/2” | 2-1/2” | 4” |
| 1,05” DE | 1,05” DE | 1,05” DE | 1,05” DE | 1,5”D-GB | Capacité en eau |
| 2m | /h32m | /h34 mois | /h34 mois | /h310m | /h3Pression de service |
| 0,15-0,6Mpa | Température de fonctionnement | ||||
| 5-50 C | Alimentation | ||||
| Pas besoin d’alimentation | No need Power | ||||
Gaskets find applications in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. In the automotive industry, gaskets are used in engines, transmissions, and exhaust systems to prevent the leakage of fluids and gases. In the aerospace industry, gaskets are crucial for maintaining airtight seals in aircraft engines and fuel systems. The oil and gas industry relies on gaskets to prevent leaks in pipelines, valves, and storage tanks. In the pharmaceutical industry, gaskets are used in equipment such as pumps and reactors to ensure the integrity of the manufacturing process. In the manufacturing sector, gaskets are used in machinery and equipment to prevent the leakage of fluids and gases, ensuring the safety and efficiency of operations.In conclusion, gaskets are indispensable components that play a vital role in various industries. Their ability to create a seal between two surfaces prevents the leakage of fluids and gases, ensuring the proper functioning of machinery and equipment. With different types and materials available, gaskets can be tailored to meet specific requirements and operating conditions. Whether it’s in the automotive, aerospace, oil and gas, pharmaceutical, or manufacturing industry, gaskets are essential for maintaining safety, efficiency, and reliability.