Understanding the Functionality of a conductivity meter
Conductivity meters are essential tools used in various industries to measure the ability of a solution to conduct electricity. This measurement is crucial in determining the purity and concentration of a solution, as well as monitoring the overall quality of water in different applications. Understanding the functionality of a conductivity meter is key to utilizing this instrument effectively.
Conductivity meters work on the principle that ions in a solution carry an electric charge, and the ability of these ions to move freely through the solution determines its conductivity. When a conductivity meter is immersed in a solution, an electric current is passed through the electrodes, and the meter measures the resistance to this current. The higher the concentration of ions in the solution, the higher the conductivity, and vice versa.

One of the key components of a conductivity meter is the electrodes. These electrodes are typically made of materials such as platinum, graphite, or stainless steel, which are good conductors of electricity. The electrodes are immersed in the solution being tested, and the conductivity meter measures the resistance between these electrodes. The conductivity meter then converts this resistance into a conductivity value, which is typically displayed in units of Siemens per centimeter (S/cm) or microsiemens per centimeter (µS/cm).
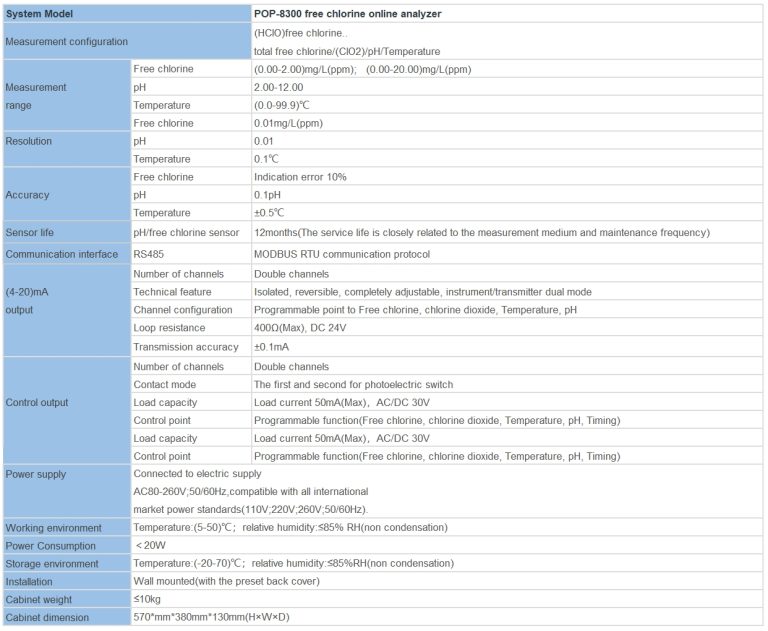
| Model | pH/ORP-510 pH/orp meter |
| Range | 0-14 pH; -2000 – +2000mV |
| Accuracy | ±0.1pH; ±2mV |
| Temp. Comp. | Manual/Automatic temperature compensation; No Comp. |
| Oper. Temp. | Normal 0~60℃; High temp 0~100℃ |
| Sensor | pH double/triple sensor; ORP sensor |
| Display | LCD Screen |
| Communication | 4-20mA output/RS485 |
| Output | High/Low limit dual relay control |
| Power | AC 220V±10% 50/60Hz or AC 110V±10% 50/60Hz or DC24V/0.5A |
| Working Environment | Ambient temperature:0~50℃ |
| Relative humidity≤85% | |
| Dimensions | 48×96×100mm(H×W×L) |
| Hole Size | 45×92mm(H×W) |
| Installation Mode | Embedded |
Calibration is an important aspect of using a conductivity meter. Calibration ensures that the meter is providing accurate and reliable measurements. Conductivity meters can be calibrated using standard solutions with known conductivity values. By immersing the electrodes in these standard solutions and adjusting the meter accordingly, users can ensure that the meter is providing accurate readings.
Conductivity meters are used in a wide range of applications, including water quality testing, environmental monitoring, food and beverage production, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and chemical processing. In water quality testing, conductivity meters are used to measure the total dissolved solids (TDS) in water, which is an indicator of water purity. In food and beverage production, conductivity meters are used to monitor the concentration of salts and other dissolved solids in various products. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, conductivity meters are used to ensure the quality and consistency of pharmaceutical products. In chemical processing, conductivity meters are used to monitor the concentration of chemicals in various processes.
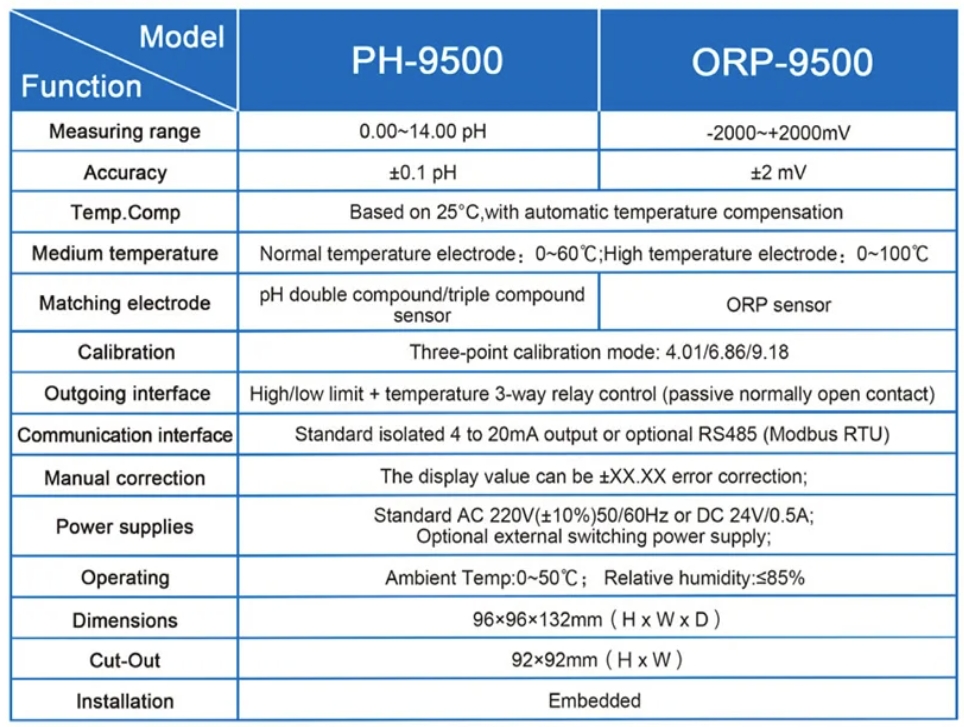
| Product name | pH/ORP-8500A transmitter controller | ||
| Measurement parameter | Measurement Range | Resolution ratio | Accuracy |
| pH | 0.00~14.00 | 0.01 | ±0.1 |
| ORP | (-1999~+1999)mV | 1mV | ±5mV(Electric meter) |
| Temperature | (0.0~100.0)℃ | 0.1℃ | ±0.5℃ |
| Temperature range of Tested solution | (0.0~100.0)℃ | ||
| Temperature component | NTC10K thermal element | ||
| (4~20)mA Current output | Channel No. | 2 channels | |
| Technical characteristics | Isolated, fully adjustable, reverse, | ||
| configurable, instrument / transmitting dual mode | |||
| Loop resistance | 400Ω(Max),DC 24V | ||
| Transmission accuracy | ±0.1mA | ||
| Control contact | Channel NO. | 3 Channels | |
| Electric contact | Semiconductor photoelectric switch | ||
| Programmable | Each channel can be programmed and point to (temperature, pH/ORP, time) | ||
| Technical characteristics | Presetting of normally open /normally closed state / pulse /PID regulation | ||
| Load capacity | 50mA(Max)AC/DC 30V | ||
| Data communication | MODBUS, RS485 standard protocol | ||
| Working power supply | DC 24V±4V | ||
| Overall power consumption | <5.5W | ||
| Working environment | Temperature: (0~50) ℃ | ||
| Relative humidity: ≤ 85%RH (non condensing) | |||
| Storage environment | Temperature: (-20~60) ℃ | ||
| Relative humidity: ≤ 85%RH (non condensing) | |||
| Protection level | IP65 (with back cover) | ||
| Shape size | 96mm×96 mm×94mm (H×W×D) | ||
| Opening size | 91mm×91mm(H×W) | ||
| Fixed mode | Panel mounting type quick fixed | ||
In conclusion, conductivity meters play a crucial role in various industries by measuring the ability of a solution to conduct electricity. By understanding the functionality of a conductivity meter and how it works, users can effectively utilize this instrument to monitor the quality of water, food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. Calibration is essential to ensure accurate measurements, and conductivity meters are used in a wide range of applications to ensure product quality and consistency. Conductivity meters are valuable tools that provide valuable insights into the composition and quality of solutions, making them indispensable in modern industry.