“Valve: Controlling flow with precision.”
Understanding the Basics of Valve Operation
Valves are essential components in various mechanical systems, playing a crucial role in controlling the flow of fluids or gases. Understanding how a valve works is fundamental to comprehending its importance and functionality in different applications.
At its core, a valve is a device that regulates, directs, or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing passageways. Valves come in different shapes, sizes, and designs, each tailored to specific requirements and operating conditions. Despite these variations, the basic principles of valve operation remain consistent across different types.
The primary function of a valve is to start, stop, or regulate the flow of a fluid within a system. This control is achieved by manipulating the position of the valve’s closure element, which can be a disc, ball, gate, or plug. When the closure element is in the closed position, it blocks the flow of fluid, preventing it from passing through the valve. Conversely, when the closure element is in the open position, it allows the fluid to flow freely through the valve.
| Model: Automatic softener Valve | ASDU2 -LCD/LED |
| Working Position | Service->Back Wash->Downflow Brine and slow rinse->Refill -> Fast rinse->Service. |
| Service->Back Wash->Upflow Brine and slow rinse->Refill -> Fast rinse->Service. | |
| Regeneration mode | Automatic type |
| Meter Delay | |
| Meter immediate | |
| Intelligent Meter Delay | |
| Intelligent Meter Immediate | |
| Timer by day : 0-99 days | |
| Timer by hours: 0-99 hours | |
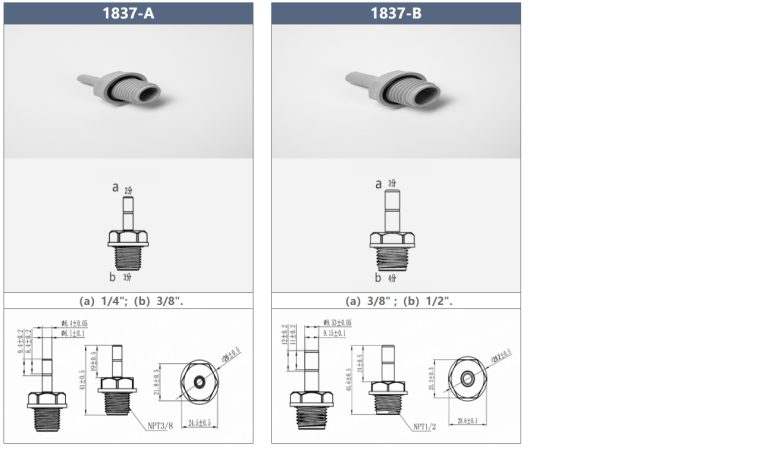
| Inlet | 1/2” 3/4” 1” |
| Outlet | 1/2” 3/4” 1” |
| Drain | 1/2” |
| Base | 2-1/2” |
| Riser pipe | 1.05” OD |
| Water Capacity | 2m3/h |
| Working Pressure | 0.15-0.6Mpa |
| Working Temperature | 5-50 °C |
| Power Supply | AC100-240 / 50-60Hz / DC12V-1.5A |
Valves operate based on the principle of pressure differentials. When the pressure on one side of the valve is higher than the pressure on the other side, the valve opens to equalize the pressure and allow the fluid to flow. Conversely, when the pressure on both sides of the valve is balanced, the valve remains closed to prevent the flow of fluid.
To control the position of the closure element, valves are equipped with actuators that can be manual, pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric. Manual valves are operated by hand, while automated valves use external energy sources to control the movement of the closure element. Actuators play a crucial role in ensuring precise and reliable valve operation, especially in complex systems where continuous monitoring and adjustment are required.
In addition to controlling the flow of fluid, valves can also be used to regulate the pressure, temperature, and direction of flow within a system. Pressure relief valves, for example, are designed to open automatically when the pressure exceeds a certain threshold, releasing excess fluid to prevent damage to the system. Similarly, temperature control valves adjust the flow of coolant or heating fluid to maintain the desired temperature within a system.

Valves are classified based on their design, function, and application. Common types of valves include gate valves, globe valves, ball valves, butterfly valves, and check valves, each serving a specific purpose in different systems. Gate valves, for instance, are used to start or stop the flow of fluid, while globe valves are ideal for regulating the flow rate within a system.
In conclusion, understanding how a valve works is essential for grasping its significance in various mechanical systems. Valves play a critical role in controlling the flow of fluids, regulating pressure and temperature, and ensuring the efficient operation of complex systems. By mastering the basics of valve operation, engineers and technicians can optimize the performance and reliability of their systems, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and productivity.