Table of Contents
Principles of Operation of a pH analyzer
A pH analyzer is a crucial instrument used in various industries to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. Understanding how a pH analyzer works is essential for ensuring accurate and reliable measurements. In this article, we will delve into the principles of operation of a pH analyzer to provide a comprehensive overview of its functionality.
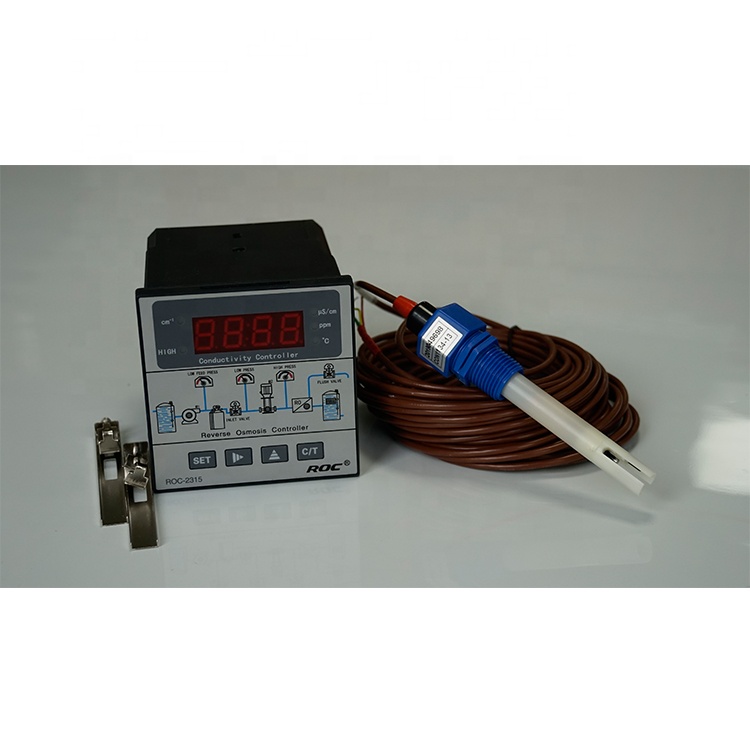
At the core of a pH analyzer is a ph sensor, which is responsible for detecting the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution. The ph sensor typically consists of a glass electrode and a reference electrode. The glass electrode is sensitive to changes in pH, while the reference electrode provides a stable reference point for comparison. When immersed in a solution, the glass electrode generates a voltage signal proportional to the pH of the solution.

The ph sensor is connected to a ph meter, which processes the voltage signal and converts it into a pH reading. The ph meter is equipped with a microprocessor that calibrates the sensor, compensates for temperature variations, and displays the pH value on a digital screen. Some pH analyzers also feature data logging capabilities, allowing users to track pH measurements over time.
One of the key principles of operation of a pH analyzer is calibration. Calibration is essential for ensuring the accuracy of pH measurements. To calibrate a pH analyzer, a series of standard buffer solutions with known pH values are used to adjust the sensor’s response. By comparing the sensor’s output to the known pH values of the buffer solutions, the pH analyzer can be calibrated to provide accurate readings.
Another important aspect of a pH analyzer is temperature compensation. pH measurements are temperature-dependent, as the ionization of water molecules changes with temperature. To account for this, pH analyzers are equipped with temperature sensors that automatically adjust the pH reading based on the temperature of the solution. This ensures that pH measurements are accurate and consistent across different temperature conditions.
In addition to calibration and temperature compensation, pH analyzers may also feature automatic cleaning and maintenance functions. Regular cleaning of the ph sensor is essential for preventing contamination and ensuring accurate measurements. Some pH analyzers are equipped with self-cleaning mechanisms that rinse the sensor with a cleaning solution to remove any buildup or deposits.
| Model | pH/ORP-8851/9900 pH/orp meter |
| Range | 0-14 pH; -2000 – +2000mV |
| Accuracy | \u00b10.1pH; \u00b12mV |
| Temp. Comp. | Automatic temperature compensation |
| Oper. Temp. | Normal 0\uff5e60\u2103; High temp 0\uff5e100\u2103 |
| Sensor | pH double/triple sensor; ORP sensor |
| Display | Big Screen LCD Screen |
| Communication | 4-20mA output/RS485 |
| Output | High/Low limit dual relay control |
| Power | DC24V/0.5A or AC85-265V\u00b110% 50/60Hz |
| Working Environment | Ambient temperature:0\uff5e50\u2103 |
| Relative humidity\u226485% | |
| Dimensions | 96\u00d796\u00d772mm(H\u00d7W\u00d7L) |
| Hole Size | 92\u00d792mm(H\u00d7W) |
| Installation Mode | Embedded |
Overall, the principles of operation of a pH analyzer involve the interaction of the ph sensor, ph meter, and various calibration and compensation mechanisms to provide accurate and reliable pH measurements. By understanding how a pH analyzer works, users can effectively monitor and control the acidity or alkalinity of solutions in a wide range of industrial applications.
In conclusion, a pH analyzer is a sophisticated instrument that plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal pH levels in various industries. By utilizing the principles of operation discussed in this article, users can ensure the accuracy and reliability of pH measurements, leading to improved process control and product quality.
Importance of Calibration and Maintenance for pH Analyzers
A pH analyzer is a crucial instrument used in various industries to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It is essential for ensuring the quality and safety of products in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and many others. Understanding how a pH analyzer works is important for ensuring accurate and reliable measurements.
A pH analyzer works by measuring the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, below 7 acidic, and above 7 alkaline. The pH analyzer consists of a probe that is immersed in the solution being tested. The probe contains a glass electrode that generates a voltage proportional to the hydrogen ion concentration in the solution. This voltage is then converted into a pH value by the analyzer.
Calibration and maintenance are essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of pH analyzers. Calibration involves adjusting the analyzer to ensure that it provides accurate measurements. This is typically done using buffer solutions with known pH values. By calibrating the analyzer with these solutions, any inaccuracies can be identified and corrected.
Regular maintenance is also important for ensuring the proper functioning of a pH analyzer. This includes cleaning the probe to remove any buildup of contaminants that could affect its performance. It is also important to check the condition of the probe and replace it if necessary. Additionally, the analyzer should be checked for any signs of wear and tear and repaired as needed.
Proper calibration and maintenance of pH analyzers are essential for ensuring the accuracy of measurements. Failure to calibrate the analyzer regularly can result in inaccurate readings, which can have serious consequences in industries where pH is a critical parameter. For example, in the food and beverage industry, incorrect pH measurements can lead to spoilage of products or even pose a health risk to consumers.
Regular maintenance is also important for prolonging the lifespan of a pH analyzer. By keeping the analyzer in good condition, it is less likely to break down or malfunction, saving time and money on repairs or replacements. Additionally, regular maintenance can help identify any issues with the analyzer before they become serious problems.
In conclusion, understanding how a pH analyzer works and the importance of calibration and maintenance is essential for ensuring accurate and reliable measurements. By calibrating the analyzer regularly and performing routine maintenance, industries can ensure the quality and safety of their products. Proper care of pH analyzers is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and effectiveness of these important instruments.