Table of Contents
Proper Usage Techniques for Conductivity Meters
Conductivity meters are essential tools used in various industries to measure the ability of a solution to conduct electricity. They are commonly used in laboratories, water treatment plants, and manufacturing facilities to ensure the quality and consistency of liquids. Proper usage of a conductivity meter is crucial to obtaining accurate and reliable results.
Before using a conductivity meter, it is important to calibrate the device to ensure its accuracy. Calibration involves adjusting the meter to a known standard solution with a specific conductivity value. This process should be done regularly to maintain the meter’s accuracy. Most conductivity meters come with calibration solutions and instructions on how to calibrate the device.
Once the conductivity meter is calibrated, it is ready to be used to measure the conductivity of a solution. To do this, first, ensure that the meter is clean and free of any debris or residue that could affect the accuracy of the readings. Rinse the probe with distilled water and dry it with a clean cloth before immersing it in the solution to be tested.
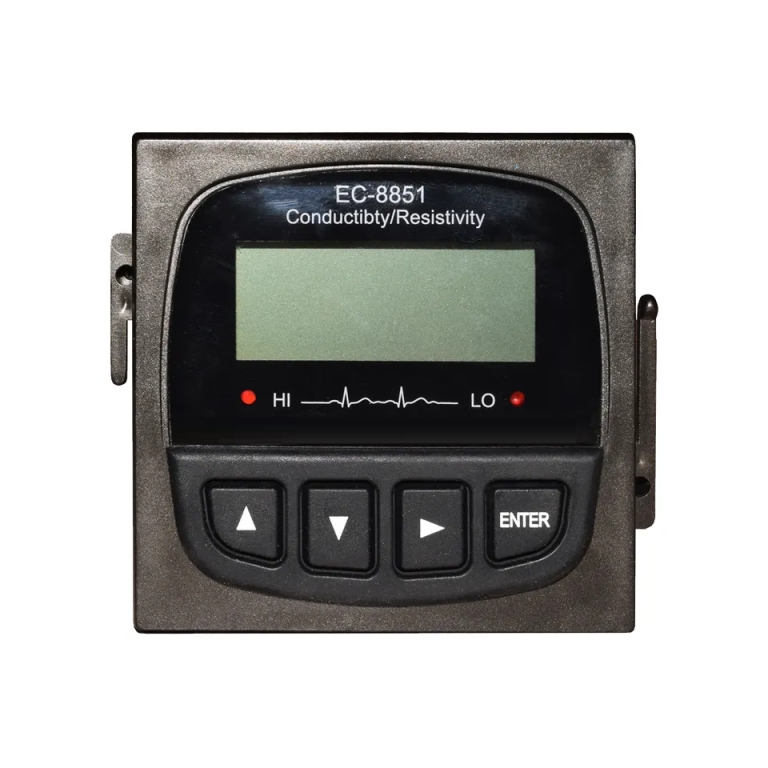
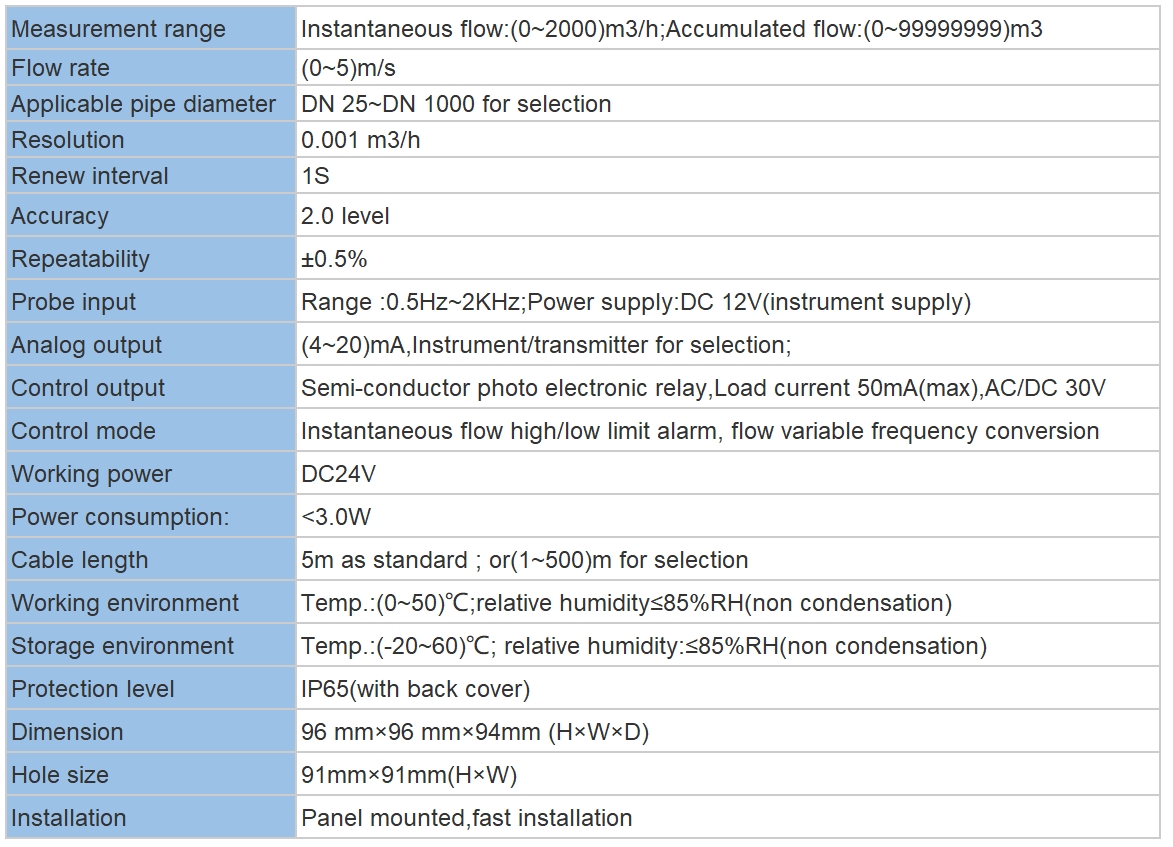
| Model | EC-8851/EC-9900 High Precision Conductivity/resistivity controller |
| Range | 0-200/2000/4000/10000uS/cm |
| 0-20/200mS/cm 0-18.25MΩ | |
| Accuracy | Conductivity:1.5%; Resistivity:2.0%(FS) |
| Temp. Comp. | Automatic temperature compensation based on 25℃ |
| Oper. Temp. | Normal 0~50℃; High temp 0~120℃ |
| Sensor | 0.01/0.02/0.1/1.0/10.0cm-1 |
| Display | LCD Screen |
| Current Output | 4-20mA output/2-10V/1-5V |
| Output | High/Low limit dual relay control |
| Power | DC24V/0.5A or |
| AC85-265V±10% 50/60Hz | |
| Working Environment | Ambient temperature:0~50℃ |
| Relative humidity≤85% | |
| Dimensions | 96×96×72mm(H×W×L) |
| Hole Size | 92×92mm(H×W) |
| Installation Mode | Embedded |
When taking a conductivity measurement, it is important to ensure that the probe is fully immersed in the solution and that there are no air bubbles trapped around the probe. Air bubbles can interfere with the conductivity measurement and lead to inaccurate results. Gently stir the solution to ensure that it is well mixed before taking the measurement.
To obtain an accurate reading, wait for the conductivity meter to stabilize before recording the measurement. The stabilization time can vary depending on the type of solution being tested and the conductivity meter being used. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for stabilization time to ensure accurate results.
After taking a conductivity measurement, it is important to clean the probe thoroughly to prevent contamination and ensure the accuracy of future measurements. Rinse the probe with distilled water and dry it with a clean cloth before storing it in a protective case to prevent damage.
In addition to proper cleaning and calibration, it is important to handle the conductivity meter with care to prevent damage. Avoid dropping the meter or exposing it to extreme temperatures or humidity, as this can affect its performance and accuracy. Store the meter in a cool, dry place when not in use to prolong its lifespan.
Regular maintenance of the conductivity meter is also important to ensure its accuracy and reliability. Check the probe for any signs of damage or wear and replace it if necessary. Keep the meter clean and calibrated regularly to maintain its accuracy.
In conclusion, proper usage techniques for conductivity meters are essential to obtaining accurate and reliable measurements. By following the manufacturer’s guidelines for calibration, measurement, cleaning, and maintenance, you can ensure that your conductivity meter performs optimally and provides accurate results. Conductivity meters are valuable tools in various industries, and proper usage techniques are crucial to maximizing their effectiveness.
Step-by-Step Guide on Using a conductivity meter
Conductivity meters are essential tools used in various industries to measure the electrical conductivity of a solution. This measurement helps determine the concentration of ions present in the solution, which is crucial for quality control and process optimization. In this article, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to use a conductivity meter effectively.
First and foremost, it is important to calibrate the conductivity meter before use. Calibration ensures the accuracy of the measurements taken by the meter. To calibrate the meter, you will need calibration standards of known conductivity levels. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions on how to calibrate the meter using these standards.
Once the meter is calibrated, you can begin using it to measure the conductivity of a solution. Start by ensuring that the meter is clean and free of any debris that could affect the accuracy of the measurements. Rinse the probe with distilled water and dry it with a clean cloth before use.
Next, immerse the probe of the conductivity meter into the solution you wish to measure. Make sure that the probe is fully submerged and that there are no air bubbles trapped around it, as this could affect the readings. Allow the meter to stabilize for a few seconds before taking the measurement.
Once the meter has stabilized, record the conductivity reading displayed on the screen. Some meters may also allow you to adjust the temperature compensation settings to account for variations in temperature that could affect the conductivity of the solution.
After taking the measurement, rinse the probe with distilled water again to remove any residue from the solution. Dry the probe thoroughly before storing it to prevent damage.
It is important to note that conductivity meters are sensitive instruments that require proper handling to ensure accurate measurements. Avoid exposing the meter to extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals that could damage the probe or affect the readings.
In addition to measuring conductivity, some meters may also have additional features such as data logging capabilities or the ability to measure other parameters such as pH or temperature. Familiarize yourself with the specific features of your meter and refer to the user manual for instructions on how to use these functions.
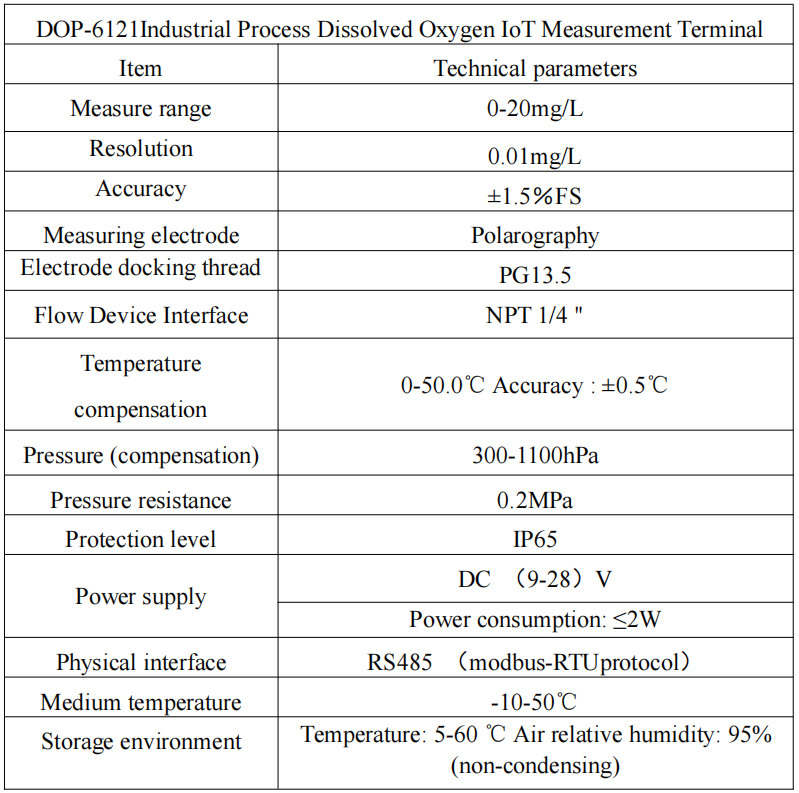
| Product Model | DOF-6310 (DOF-6141) |
| Product Name | Dissolved oxygen data collection terminal |
| Measuring Method | Fluorescence Method |
| Measurement range | 0-20mg/L |
| Accuracy | ±0.3mg/L |
| Resolution | 0.01mg/L |
| Response time | 90s |
| Repeatibility | 5%RS |
| Temperature compensation | 0-60.0℃ Accuracy:±0.5℃ |
| Air pressure compensation | 300-1100hPa |
| Stand pressure | 0.3Mpa |
| Communication | RS485 MODBUS-RTU standard protocol |
| Power | DC(9-28)V |
| Power comsuption | <2W |
| Operational envrionment | Temperature:(0-50)℃ |
| Storage Environment | Temperature:(-10-60)℃; Humidity:≤95%RH(None condensation) |
| Installation | Submerged |
| Protection Level | IP68 |
| Weight | 1.5Kg(with 10m cable) |
In conclusion, conductivity meters are valuable tools for measuring the electrical conductivity of solutions in various industries. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively use a conductivity meter to obtain accurate measurements and ensure the quality of your products or processes. Remember to calibrate the meter before use, handle it with care, and refer to the user manual for any additional features or functions. With proper use and maintenance, a conductivity meter can be a reliable tool for monitoring and controlling the conductivity of solutions in your industry.






