“Accurate measurements, precise results – the power of ph meter electrodes.”
Understanding the Basics of ph meter Electrodes
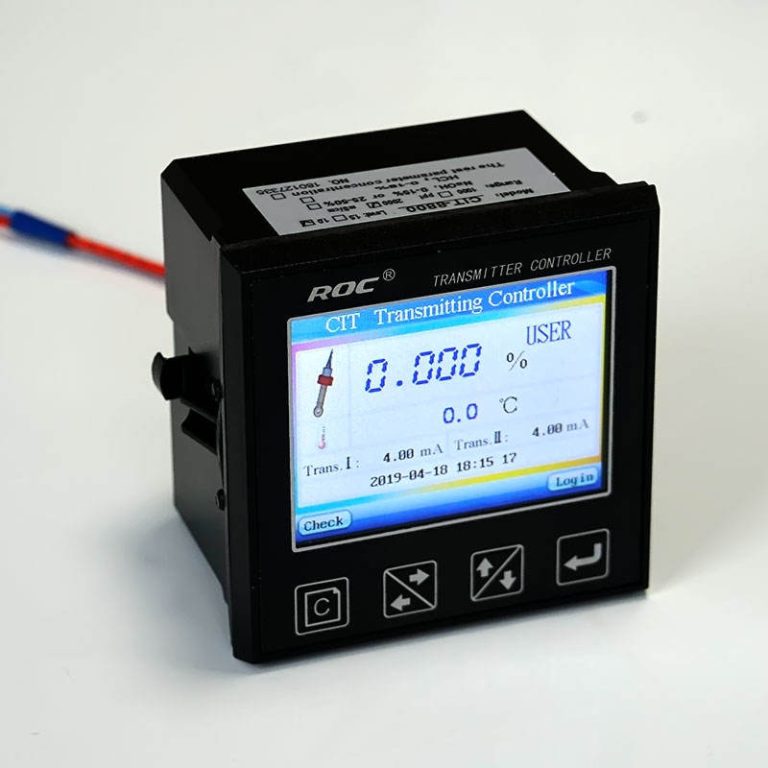
A ph meter electrode is a crucial component of a ph meter, a device used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. Understanding how a ph meter electrode works is essential for anyone using a ph meter for scientific research, quality control, or other applications.

The ph meter electrode consists of a glass membrane that is sensitive to hydrogen ions in the solution being tested. When the electrode is immersed in a solution, hydrogen ions in the solution interact with the glass membrane, causing a potential difference to develop between the inside and outside of the electrode. This potential difference is measured by the ph meter and used to calculate the pH of the solution.
The glass membrane of the ph meter electrode is typically made of a special type of glass that is selective to hydrogen ions. This glass is usually doped with metal oxides such as lithium or sodium to enhance its sensitivity to hydrogen ions. The glass membrane is porous, allowing hydrogen ions to pass through and interact with the internal reference solution of the electrode.
The internal reference solution of the ph meter electrode is typically a solution of known pH, such as a buffer solution. This reference solution helps to maintain a stable potential difference between the inside and outside of the electrode, ensuring accurate pH measurements. The reference solution is separated from the sample solution by the glass membrane, preventing contamination of the reference solution by the sample solution.

When the ph meter electrode is immersed in a solution, hydrogen ions in the solution diffuse through the glass membrane and interact with the internal reference solution. This interaction causes a potential difference to develop between the inside and outside of the electrode, which is measured by the ph meter. The ph meter then converts this potential difference into a pH value using a calibration curve.
Calibration of a ph meter electrode is essential for accurate pH measurements. Calibration involves immersing the electrode in solutions of known pH, typically pH 4, 7, and 10, and adjusting the ph meter to match the pH values of these solutions. This calibration process ensures that the ph meter electrode is accurately measuring the pH of the sample solution.
| Measuring Method | N,N-Diethyl-1,4-phenylenediamine (DPD) spectrophotometry | |||
| Model | CLA-7122 | CLA-7222 | CLA-7123 | CLA-7223 |
| Inlet water channel | Single channel | Dual channel | Single channel | Dual channel |
| Measurement range | Total Chlorine : (0.0 ~ 2.0)mg/L ,calculated as Cl2 ; | Total Chlorine : (0.5 ~10.0)mg/L ,calculated as Cl2 ; | ||
| pH:(0-14);temperature:(0-100)℃ | ||||
| Accuracy | Free chlorine: ±10% or 0.05mg/L (whichever is greater), calculated as Cl2; Total chlorine: ±10% or 0.05mg/L (whichever is greater), calculated as Cl2 | Free chlorine: ±10% or 0.25mg/L (whichever is greater), calculated as Cl2; Total chlorine: ±10% or 0.25mg/L (whichever is greater), calculated as Cl2 | ||
| pH:±0.1pH;Temp.:±0.5℃ | ||||
| Measurement cycle | Free Chlorine≤2.5min | |||
| Sampling interval | The interval (1~999) min can be set to any value | |||
| Maintenance cycle | Recommended once a month (see maintenance chapter) | |||
| Environmental | Ventilated and dry room without strong vibration; Suggested room temperature: (15 ~ 28)℃; relative humidity: ≤85% (no condensation). | |||
| requirements | ||||
| Sample water flow | (200-400) mL/min | |||
| inlet water pressure | (0.1-0.3) bar | |||
| Inlet water temperature range | (0-40)℃ | |||
| Power supply | AC (100-240)V; 50/60Hz | |||
| Consumption | 120W | |||
| Power connection | 3-core power cord with plug is connected to the mains socket with ground wire | |||
| Data output | RS232/RS485/(4~20)mA | |||
| Dimension size | H*W*D:(800*400*200)mm | |||
In addition to the glass membrane electrode, there are other types of ph meter electrodes, such as solid-state electrodes and combination electrodes. Solid-state electrodes use a solid-state sensor instead of a glass membrane to measure pH, while combination electrodes combine a pH electrode with a reference electrode in a single housing.
| CCT-3300 | ||||
| Constant | 10.00cm-1 | 1.000cm-1 | 0.100cm-1 | 0.010cm-1 |
| Conductivity | (500~20,000) | (1.0~2,000) | (0.5~200) | (0.05~18.25) |
| μS/cm | μS/cm | μS/cm | MΩ·cm | |
| TDS | (250~10,000) | (0.5~1,000) | (0.25~100) | —— |
| ppm | ppm | ppm | ||
| Medium Temp. | (0~50)℃(Temp. Compensation : NTC10K) | |||
| Resolution | Conductivity: 0.01μS/cm;0.01mS/cm | |||
| TDS: 0.01ppm | ||||
| Temp.: 0.1℃ | ||||
| Accuracy | Conductivity:1.5%(FS) | |||
| Resistivity: 2.0%(FS) | ||||
| TDS:1.5%(FS) | ||||
| Temp:±0.5℃ | ||||
| Analog Output | Single isolated(4~20)mA,instrument/transmitter for selection | |||
| Control Output | SPDT relay,Load Capacity: AC 230V/50A(Max) | |||
| Working Environment | Temp: (0~50)℃;Relative humidity: ≤85%RH(none condensation) | |||
| Storage Environment | Temp:(-20~60)℃; Relative humidity ≤85%RH(none condensation) | |||
| Power Supply | DC 24V/AC 110V/AC 220V±15%(for selection) | |||
| Dimension | 48mm×96mm×80mm (H×W×D) | |||
| Hole Size | 44mm×92mm (H×W) | |||
| Installation | Panel mounted, fast installation | |||
In conclusion, a ph meter electrode works by using a glass membrane that is sensitive to hydrogen ions in a solution. When the electrode is immersed in a solution, hydrogen ions interact with the glass membrane, causing a potential difference to develop between the inside and outside of the electrode. This potential difference is measured by the ph meter and used to calculate the pH of the solution. Calibration of the ph meter electrode is essential for accurate pH measurements, and there are different types of ph meter electrodes available for various applications. Understanding how a ph meter electrode works is essential for anyone using a ph meter for pH measurements.