pH: Keep it balanced, keep it safe.
ORP: Optimal levels for a sparkling pool.
Table of Contents
Proper pH Levels for Your Pool
Maintaining proper pH levels in your pool is essential for ensuring the health and safety of swimmers, as well as the longevity of your pool equipment. pH, which stands for potential of hydrogen, is a measure of how acidic or basic the water in your pool is. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A pH level below 7 indicates acidic water, while a pH level above 7 indicates basic water.
| Model | FL-9900 Paddle Wheel flow meter |
| Range | Flow Speed:0.5-5 m/s |
| Instantaneous Flow:0-2000m3/h | |
| Accuracy | Level 2 |
| Temp. Comp. | Automatic temperature compensation |
| Oper. Temp. | Normal 0~60℃; High temp 0~100℃ |
| Sensor | Paddle Wheel Sensor |
| Pipeline | DN20-DN300 |
| Communication | 4-20mA output/RS485 |
| Control | Instantaneous Flow High/Low alarm |
| Load Current 5A(Max) | |
| Power | 220V/110V/24V |
| Working Environment | Ambient temperature:0~50℃ |
| Relative humidity≤85% | |
| Dimensions | 96×96×72mm(H×W×L) |
| Hole Size | 92×92mm(H×W) |
| Installation Mode | Embedded |
Ideally, the pH level in your pool should be between 7.2 and 7.6. This range is considered optimal for swimming comfort and effectiveness of pool chemicals. If the pH level is too low, the water can be corrosive and damage pool equipment, irritate swimmers’ skin and eyes, and reduce the effectiveness of chlorine. On the other hand, if the pH level is too high, the water can become cloudy, scale can form on pool surfaces, and chlorine will be less effective at killing bacteria and algae.
To maintain the proper pH level in your pool, it is important to test the water regularly using a pool test kit. These kits are readily available at pool supply stores and are easy to use. Once you have tested the water, you can adjust the pH level by adding pH increaser (sodium carbonate) to raise the pH or pH decreaser (sodium bisulfate) to lower the pH. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when adding these chemicals to your pool to avoid overcorrection.

In addition to pH, another important factor to consider when maintaining your pool is ORP, which stands for oxidation-reduction potential. ORP measures the ability of the water to oxidize contaminants, such as bacteria and algae. The ideal ORP level for a pool is between 650 and 750 millivolts. If the ORP level is too low, the water may not be effectively sanitized, leading to cloudy water and potential health risks for swimmers. If the ORP level is too high, the water may be over-sanitized, leading to eye and skin irritation for swimmers.
To maintain the proper ORP level in your pool, it is important to ensure that your chlorine levels are within the recommended range. Chlorine is the most common sanitizer used in pools and plays a crucial role in maintaining water quality. The recommended chlorine level for a pool is between 1 and 3 parts per million (ppm). You can test the chlorine level in your pool using a pool test kit and adjust it by adding chlorine tablets or liquid chlorine as needed.
In conclusion, maintaining proper pH and ORP levels in your pool is essential for ensuring the health and safety of swimmers, as well as the longevity of your pool equipment. By regularly testing the water and making adjustments as needed, you can enjoy a clean and clear pool all season long. Remember to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when adding chemicals to your pool and consult a professional if you are unsure about how to maintain the proper levels. With proper care and attention, you can keep your pool in top condition for years to come.
Understanding ORP Levels in Pool Water
Maintaining proper pH and ORP levels in a pool is essential for ensuring the water is safe and comfortable for swimmers. pH refers to the acidity or alkalinity of the water, while ORP (Oxidation-Reduction Potential) measures the ability of the water to break down contaminants. Both factors play a crucial role in the overall water quality of a pool.

The ideal pH level for pool water is between 7.2 and 7.6. This range is considered optimal because it is close to the pH of human tears and saliva, making it comfortable for swimmers. If the pH level is too low (below 7.2), the water can become acidic, leading to skin and eye irritation. On the other hand, if the pH level is too high (above 7.6), the water can become alkaline, which can also cause skin and eye irritation.
In addition to pH, ORP levels are also important for maintaining clean and safe pool water. ORP measures the ability of the water to break down contaminants, such as bacteria and algae. The ideal ORP level for pool water is between 650 and 750 mV (millivolts). This range ensures that the water is effectively sanitizing and disinfecting itself, keeping it free from harmful microorganisms.
It is important to note that pH and ORP levels are interrelated. If the pH level is too high or too low, it can affect the ORP level of the water. For example, if the pH level is too high, the ORP level may be lower than optimal, reducing the water’s ability to sanitize itself effectively. Conversely, if the pH level is too low, the ORP level may be higher than optimal, which can lead to over-sanitization and potential damage to pool equipment.
To maintain proper pH and ORP levels in a pool, regular testing and adjustments are necessary. Pool owners should test the water at least once a week using a reliable test kit or electronic monitor. If the pH or ORP levels are outside the recommended range, appropriate adjustments should be made using pH increasers or decreasers, as well as oxidizing agents such as chlorine or bromine.
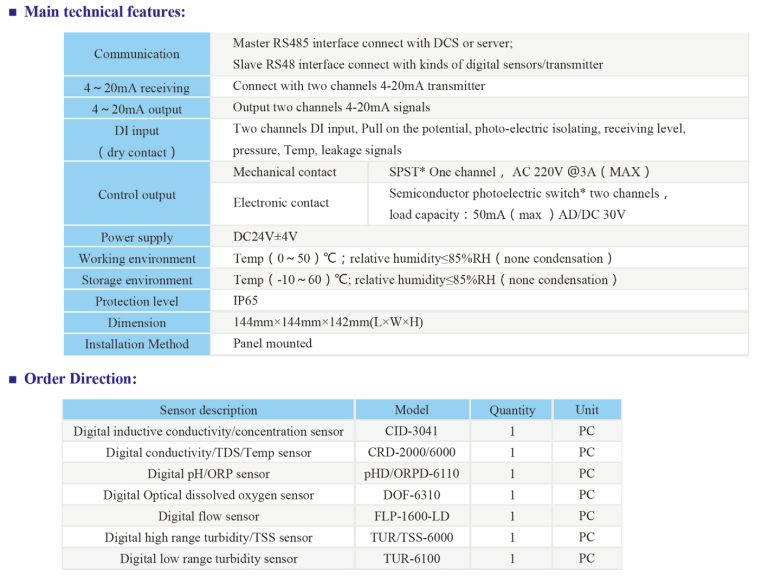
| Model | CIT-8800 Inductive Conductivity/Concentration Oline Controller |
| Concentration | 1.NaOH:(0~15)% or(25~50)%; 2.HNO3:(0~25)% or(36~82)%; 3.User-defined concentration curves |
| Conductivity | (500~2,000,000)uS/cm |
| TDS | (250~1,000,000)ppm |
| Temp. | (0~120)°C |
| Resolution | Conductivity: 0.01uS/cm; Concentration: 0.01%; TDS:0.01ppm, Temp.: 0.1℃ |
| Accuracy | Conductivity: (500~1000)uS/cm +/-10uS/cm; (1~2000)mS/cm+/-1.0% |
| TDS: 1.5 level, Temp.: +/-0.5℃ | |
| Temp. compensation | Range: (0~120)°C; element: Pt1000 |
| Communication port | RS485.Modbus RTU protocol |
| Analog output | Two channels isolated/ transportable (4-20)mA, Instrument / Transmitter for selection |
| Control Output | Triple channels semiconductor photoelectric switch, Programmable Switch, pulse and frequency |
| Working Environment | Temp.(0~50)℃; relative humidity <95%RH (non-condensing) |
| Storage Environment | Temp.(-20~60)℃;Relative Humidity ≤85%RH (none condensation) |
| Power Supply | DC 24V+15% |
| Protection Level | IP65 (with rear cover) |
| Dimension | 96mmx96mmx94mm(HxWxD) |
| Hole Size | 9lmmx91mm(HxW) |
In addition to regular testing, other factors can also affect pH and ORP levels in pool water. These include the number of swimmers, weather conditions, and the use of pool chemicals. For example, heavy rainfall can dilute the pool water, affecting its pH and ORP levels. Similarly, a high bather load can introduce contaminants into the water, requiring more frequent testing and adjustments.
In conclusion, maintaining proper pH and ORP levels in a pool is essential for ensuring clean, safe, and comfortable water for swimmers. By monitoring and adjusting these levels regularly, pool owners can enjoy a healthy and enjoyable swimming experience. Remember, a little effort in maintaining pH and ORP levels can go a long way in keeping your pool water crystal clear and inviting.