Table of Contents
The Importance of Regular Water Potability Testing for Homeowners
Water potability testing is a crucial aspect of maintaining a safe and healthy home environment. Potable water is water that is safe for human consumption, meaning it meets certain quality standards set by regulatory agencies. Regular testing of your home’s water supply is essential to ensure that it is free from harmful contaminants and bacteria that could pose a risk to your health.
One of the main reasons why regular water potability testing is important for homeowners is to protect the health of their families. Contaminated water can contain harmful bacteria, viruses, and chemicals that can cause a range of health problems, from gastrointestinal issues to more serious illnesses. By testing your water regularly, you can identify any potential contaminants and take steps to address them before they become a health hazard.
In addition to protecting your health, regular water potability testing can also help you identify any issues with your home’s plumbing or water supply system. For example, high levels of certain minerals in your water can indicate corrosion in your pipes, which can lead to leaks and other plumbing problems. By testing your water regularly, you can catch these issues early and prevent costly repairs down the line.
Another important reason to regularly test your home’s water supply is to ensure compliance with local regulations. Many municipalities have specific guidelines for water quality that homeowners must adhere to. By testing your water regularly, you can ensure that you are meeting these standards and avoid any potential fines or penalties for non-compliance.
When it comes to testing your water for potability, there are a few key contaminants that you should be on the lookout for. These include bacteria such as E. coli and coliform, which can indicate fecal contamination in your water supply. Other common contaminants to test for include lead, arsenic, nitrates, and pesticides, all of which can have serious health effects if present in high levels.
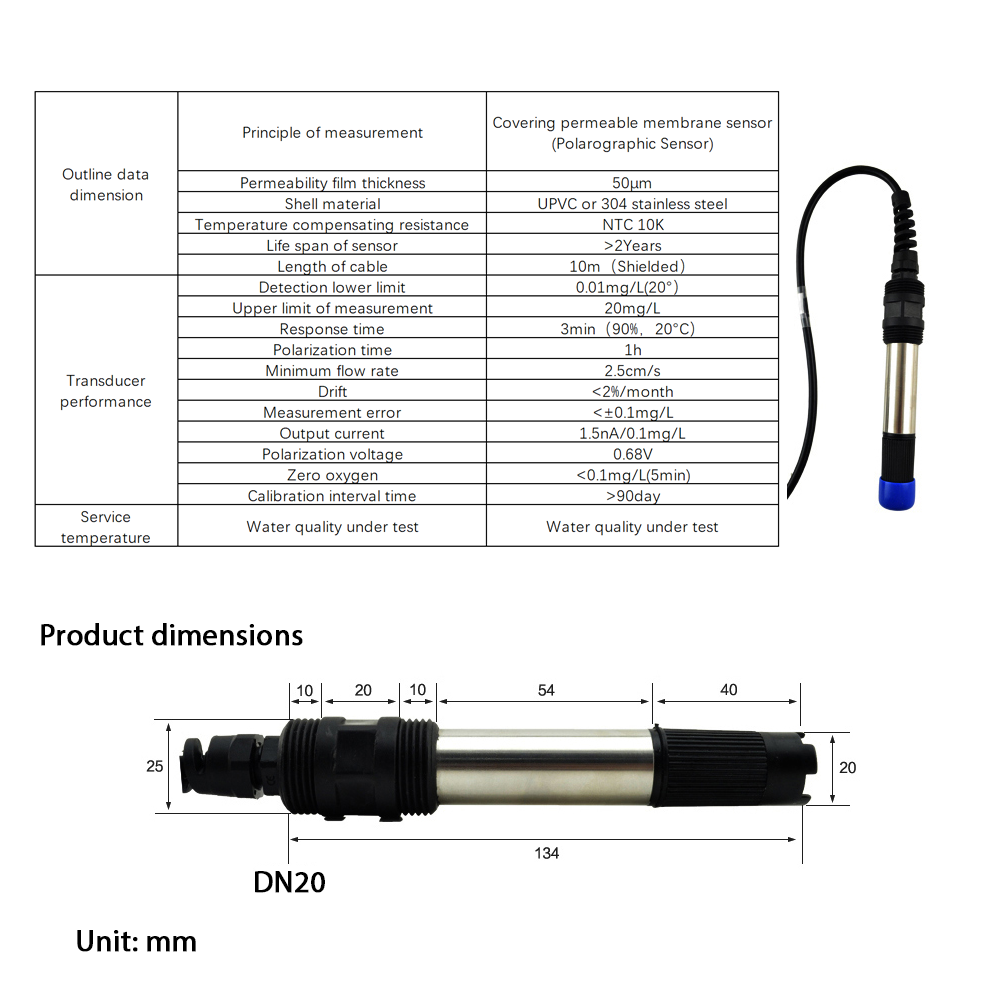

There are several ways to test your home’s water for potability, including DIY test kits that you can purchase online or at your local hardware store. These kits typically involve collecting a water sample from your tap and sending it off to a lab for analysis. Alternatively, you can hire a professional water testing company to come to your home and conduct a more comprehensive analysis of your water supply.
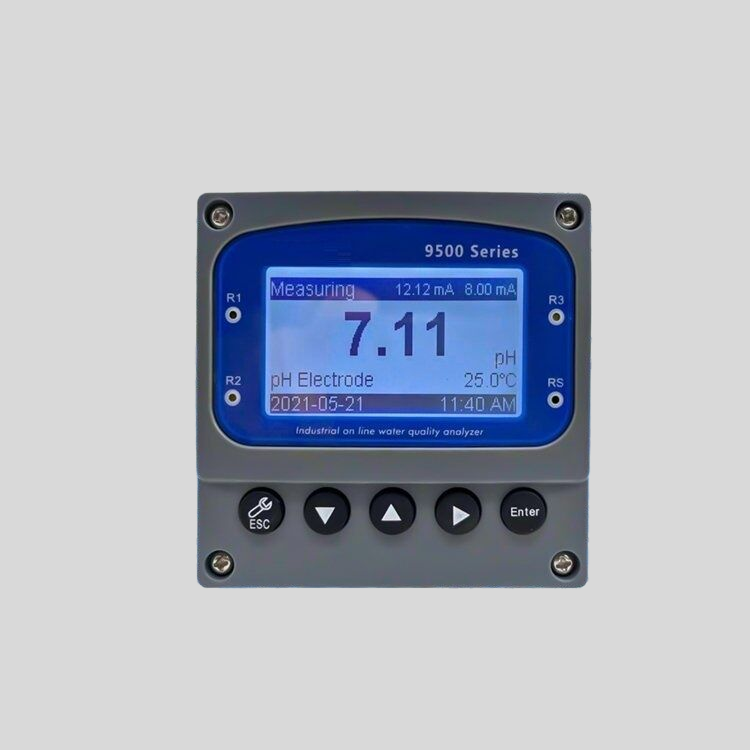
| POP-8300 free chlorine online analyzer | ||
| System Model | POP-8300 free chlorine online analyzer | |
| Measurement configuration | (HClO)free chlorine.. | |
| total free chlorine/(ClO2)/pH/Temperature | ||
| Free chlorine | (0.00-2.00)mg/L(ppm); (0.00-20.00)mg/L(ppm) | |
| Measurement | pH | 2.00-12.00 |
| range | Temperature | (0.0-99.9)℃ |
| Free chlorine | 0.01mg/L(ppm) | |
| Resolution | pH | 0.01 |
| Temperature | 0.1℃ | |
| Free chlorine | Indication error 10% | |
| Accuracy | pH | 0.1pH |
| Temperature | ±0.5℃ | |
| Sensor life | pH/free chlorine sensor | 12months(The service life is closely related to the measurement medium and maintenance frequency) |
| Communication interface | RS485 | MODBUS RTU communication protocol |
| Number of channels | Double channels | |
| (4-20)mA | Technical feature | Isolated, reversible, completely adjustable, instrument/transmitter dual mode |
| output | Channel configuration | Programmable point to Free chlorine, chlorine dioxide, Temperature, pH |
| Loop resistance | 400Ω(Max), DC 24V | |
| Transmission accuracy | ±0.1mA | |
| Number of channels | Double channels | |
| Contact mode | The first and second for photoelectric switch | |
| Control output | Load capacity | Load current 50mA(Max),AC/DC 30V |
| Control point | Programmable function(Free chlorine, chlorine dioxide, Temperature, pH, Timing) | |
| Load capacity | Load current 50mA(Max),AC/DC 30V | |
| Control point | Programmable function(Free chlorine, chlorine dioxide, Temperature, pH, Timing) | |
| Power supply | Connected to electric supply | |
| AC80-260V;50/60Hz,compatible with all international | ||
| market power standards(110V;220V;260V;50/60Hz). | ||
| Working environment | Temperature:(5-50)℃;relative humidity:≤85% RH(non condensation) | |
| Power Consumption | <20W | |
| Storage environment | Temperature:(-20-70)℃;relative humidity:≤85%RH(non condensation) | |
| Installation | Wall mounted(with the preset back cover) | |
| Cabinet weight | ≤10kg | |
| Cabinet dimension | 570*mm*380mm*130mm(H×W×D) | |
In conclusion, regular water potability testing is an essential part of maintaining a safe and healthy home environment. By testing your water regularly, you can protect the health of your family, identify any issues with your plumbing or water supply system, ensure compliance with local regulations, and ultimately have peace of mind knowing that your water is safe to drink. Don’t wait until it’s too late – schedule a water potability test for your home today.
Understanding the Process and Results of Water Potability Testing
Water potability testing is a crucial process that helps ensure the safety and quality of drinking water. This testing is conducted to determine if water meets the standards set by regulatory agencies for human consumption. Understanding the process and results of water potability testing is essential for both consumers and water providers.
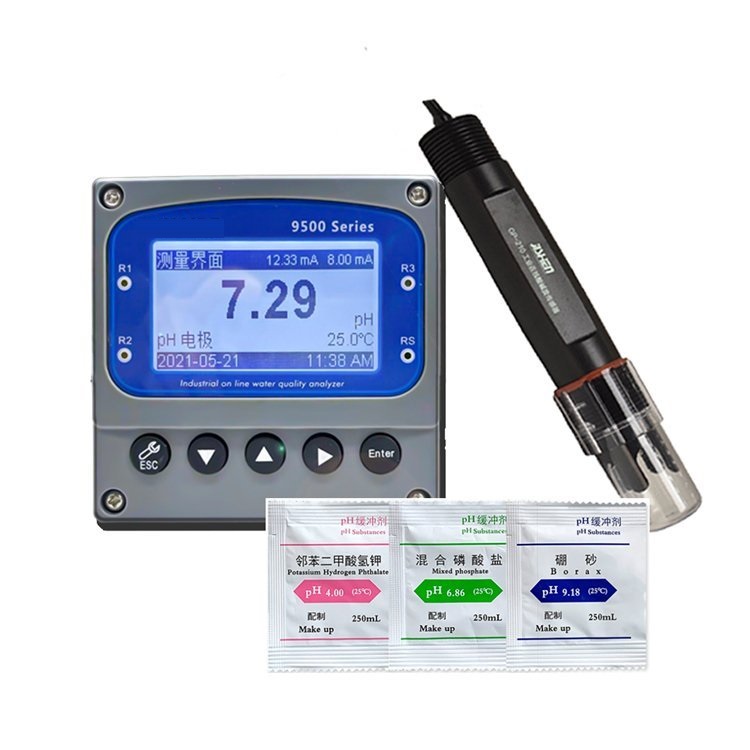
| pH/ORP-3500 series pH/ORP Online Meter | |||
| pH | ORP | Temp. | |
| Measurement range | 0.00~14.00 | (-2000~+2000)mV | (0.0~99.9)℃(Temp. Compensation :NTC10K) |
| Resolution | 0.01 | 1mV | 0.1℃ |
| Accuracy | ±0.1 | ±5mV(electronic unit) | ±0.5℃ |
| Buffer Solution | 9.18;6.86;4.01;10.00;7.00;4.00 | ||
| Medium Temp. | (0~50)℃(with 25℃ as standard )manual / automatic temp.compensation for selection | ||
| Analog Output | Isolated one Channel(4~20)mA,Instrument / Transmitter for selection | ||
| Control Output | Double relay output(ON/OFF) | ||
| Consumption | <3W | ||
| Working Environment | Working temp. (0~50)℃;Relative humidity≤85%RH(none condensation) | ||
| Storage Environment | Temp. (-20~60)℃; Relative humidity≤85%RH(none condensation) | ||
| Dimension | 48mm×96mm×80mm (H×W×D) | ||
| Hole Size | 44mm×92mm (H×W) | ||
| Installation | Panel mounted ,fast installation | ||
The first step in water potability testing is sample collection. Samples are typically collected from various points in the water distribution system, including treatment plants, storage tanks, and residential taps. It is important to collect samples in clean, sterile containers to prevent contamination. Once collected, samples are transported to a certified laboratory for analysis.
In the laboratory, samples are tested for a variety of contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, chemicals, and heavy metals. One of the most common tests conducted is for coliform bacteria, which are indicators of potential fecal contamination. High levels of coliform bacteria in water can indicate the presence of harmful pathogens that can cause illness.
Chemical testing is also important in water potability testing. Chemical contaminants such as lead, arsenic, and pesticides can pose serious health risks if present in drinking water. These contaminants can enter the water supply through industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, or aging infrastructure. Regular testing for chemical contaminants is essential to ensure the safety of drinking water.
Once testing is complete, the laboratory will provide a report detailing the results of the analysis. This report will indicate whether the water meets the regulatory standards for potability. If any contaminants are detected above the allowable limits, corrective actions must be taken to address the issue.
Interpreting the results of water potability testing can be complex, as there are many factors to consider. It is important to understand the regulatory standards for drinking water in your area and how the test results compare to these standards. If contaminants are detected, it is important to determine the source of the contamination and take appropriate measures to address it.
In some cases, water treatment may be necessary to remove contaminants and ensure the safety of the water supply. Common treatment methods include filtration, disinfection, and chemical treatment. It is important to work with a qualified water treatment professional to determine the most effective treatment options for your specific situation.
Regular monitoring and testing of drinking water are essential to ensure its safety and quality. Water potability testing should be conducted on a routine basis to detect any changes in water quality and address potential issues before they become a health risk. By staying informed about the process and results of water potability testing, consumers can take proactive steps to protect their health and well-being.