“ph meter: Accurate measurements for optimal results. Works by measuring the acidity or alkalinity of a solution using a glass electrode.”
Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics of ph meter
A ph meter is a crucial tool used in various industries, including agriculture, food and beverage production, pharmaceuticals, and environmental monitoring. It measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution by determining the concentration of hydrogen ions present. Understanding how a ph meter works is essential for accurate and reliable measurements.
The basic principle behind a ph meter is the measurement of the electrical potential difference between a reference electrode and a glass electrode. The glass electrode is sensitive to hydrogen ions in the solution, while the reference electrode provides a stable reference point for comparison. When the glass electrode comes into contact with a solution, it generates a voltage that is proportional to the pH of the solution.

To ensure accurate measurements, the ph meter must be calibrated using buffer solutions with known pH values. This calibration process allows the ph meter to establish a linear relationship between the voltage generated by the glass electrode and the pH of the solution being measured. Once calibrated, the ph meter can accurately determine the pH of unknown solutions by comparing the voltage generated by the glass electrode to the calibration curve.
The ph meter typically displays the pH value on a digital screen, making it easy for users to read and record the results. Some advanced pH meters also offer additional features, such as temperature compensation and automatic calibration, to improve accuracy and convenience.
In addition to measuring the pH of a solution, pH meters can also be used to monitor changes in pH over time. This is particularly useful in processes where maintaining a specific pH range is critical, such as in chemical reactions or fermentation processes. By continuously monitoring the pH of a solution, operators can make real-time adjustments to ensure optimal conditions for their processes.
| ROS-2210 Double-Stage Reverse Osmosis Program Controller | |
| 1.water source water tank without water protection | |
| 2. Pure tank low level | |
| 3.Pure tank high level | |
| Acquisition signal | 4.low pressure protection |
| 5.high pressure protection | |
| 6.pretreatment regeneration | |
| 7.manual/automatic control | |
| 1.water inlet valve | |
| 2. flush valve | |
| Output control | 3. low pressure pump |
| 4.high pressure pump | |
| 5.conductivity over standard valve | |
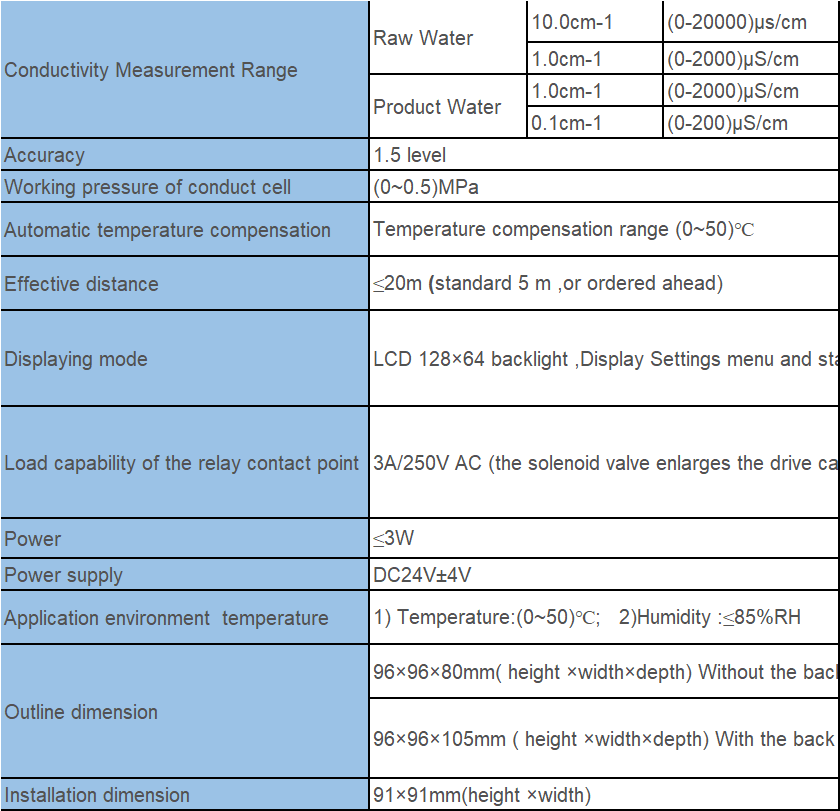
| Measuring range | 0~2000uS |
| Temperature range | Based on 25℃, automatic temperature compensation |
| AC220v±10% 50/60Hz | |
| Power supply | AC110v±10% 50/60Hz |
| DC24v±10% | |
| Medium temperature | The normal temperature electrode<60℃ |
| High temperature electrode<120℃ | |
| Control output | 5A/250V AC |
| Relative humidity | ≤85% |
| Ambient temperature | 0~50℃ |
| Hole Size | 92*92mm(high*wide) |
| Installation method | The embedded |
| Cell constant | 1.0cm-¹*2 |
| Display usage | Digital display: conductivity value/temperature value; Supporting RO process flow chart |
| 1.Electrode constant and type setting | |
| 2.Conductivity overrun setting | |
| 3.Flush Settings at intervals of * hours | |
| Main function | 4.Flushing time setting |
| 5.RO membrane running time setting | |
| 6.Power on automatic operation/stop setting | |
| 7.Mailing address, baud rate setting | |
| 8.Optional RS-485 communication interface | |
One of the key advantages of using a ph meter is its versatility and ease of use. With proper calibration and maintenance, pH meters can provide accurate and reliable measurements across a wide range of applications. Whether you are a scientist conducting research in a laboratory or a farmer monitoring soil pH in the field, a ph meter is an indispensable tool for ensuring the quality and consistency of your products.
In conclusion, a ph meter is a valuable instrument for measuring the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. By understanding how a ph meter works and following proper calibration procedures, users can obtain accurate and reliable pH measurements for a variety of applications. Whether you are a novice user or an experienced professional, a ph meter is an essential tool for ensuring the success of your work.
Exploring the Functionality of ph meter
A ph meter is a crucial tool used in various industries, including agriculture, food and beverage production, pharmaceuticals, and environmental monitoring. It is an instrument that measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, providing valuable information about the chemical composition of the substance being tested. Understanding how a ph meter works is essential for obtaining accurate and reliable results in scientific research and industrial processes.
The ph meter operates on the principle of measuring the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, below 7 acidic, and above 7 alkaline. The ph meter consists of a glass electrode and a reference electrode immersed in the solution being tested. The glass electrode is sensitive to changes in hydrogen ion concentration, while the reference electrode provides a stable reference point for comparison.
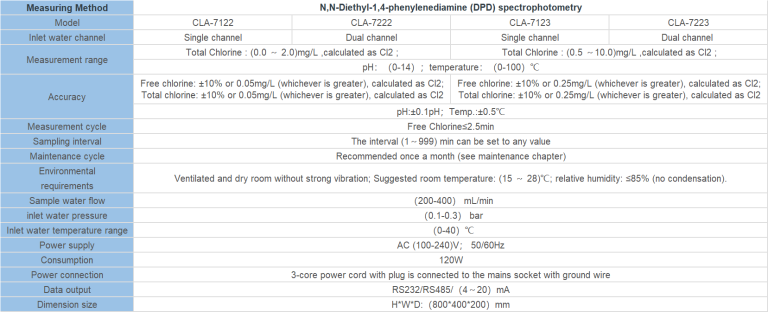
| POP-8300 free chlorine online analyzer | ||
| System Model | POP-8300 free chlorine online analyzer | |
| Measurement configuration | (HClO)free chlorine.. | |
| total free chlorine/(ClO2)/pH/Temperature | ||
| Free chlorine | (0.00-2.00)mg/L(ppm); (0.00-20.00)mg/L(ppm) | |
| Measurement | pH | 2.00-12.00 |
| range | Temperature | (0.0-99.9)℃ |
| Free chlorine | 0.01mg/L(ppm) | |
| Resolution | pH | 0.01 |
| Temperature | 0.1℃ | |
| Free chlorine | Indication error 10% | |
| Accuracy | pH | 0.1pH |
| Temperature | ±0.5℃ | |
| Sensor life | pH/free chlorine sensor | 12months(The service life is closely related to the measurement medium and maintenance frequency) |
| Communication interface | RS485 | MODBUS RTU communication protocol |
| Number of channels | Double channels | |
| (4-20)mA | Technical feature | Isolated, reversible, completely adjustable, instrument/transmitter dual mode |
| output | Channel configuration | Programmable point to Free chlorine, chlorine dioxide, Temperature, pH |
| Loop resistance | 400Ω(Max), DC 24V | |
| Transmission accuracy | ±0.1mA | |
| Number of channels | Double channels | |
| Contact mode | The first and second for photoelectric switch | |
| Control output | Load capacity | Load current 50mA(Max),AC/DC 30V |
| Control point | Programmable function(Free chlorine, chlorine dioxide, Temperature, pH, Timing) | |
| Load capacity | Load current 50mA(Max),AC/DC 30V | |
| Control point | Programmable function(Free chlorine, chlorine dioxide, Temperature, pH, Timing) | |
| Power supply | Connected to electric supply | |
| AC80-260V;50/60Hz,compatible with all international | ||
| market power standards(110V;220V;260V;50/60Hz). | ||
| Working environment | Temperature:(5-50)℃;relative humidity:≤85% RH(non condensation) | |
| Power Consumption | <20W | |
| Storage environment | Temperature:(-20-70)℃;relative humidity:≤85%RH(non condensation) | |
| Installation | Wall mounted(with the preset back cover) | |
| Cabinet weight | ≤10kg | |
| Cabinet dimension | 570*mm*380mm*130mm(H×W×D) | |
When the glass electrode comes into contact with the solution, it generates a voltage proportional to the hydrogen ion concentration. This voltage is then converted into a pH value by the ph meter, which displays the result on a digital screen. The accuracy of the measurement depends on the calibration of the ph meter, which is typically done using buffer solutions with known pH values.
One of the key components of a ph meter is the glass electrode, which is made of a special type of glass that is sensitive to changes in pH. The glass electrode contains a thin membrane that allows hydrogen ions to pass through, creating an electrical potential that is measured by the ph meter. The reference electrode, on the other hand, is typically made of a stable metal such as silver-silver chloride, which provides a constant reference point for comparison.
Calibrating a ph meter is essential for obtaining accurate and reliable results. This is done by immersing the electrodes in buffer solutions with known pH values and adjusting the meter accordingly. Most pH meters have a calibration function that allows users to easily calibrate the instrument before each use. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration to ensure the accuracy of the measurements.
In addition to calibration, proper maintenance of the ph meter is essential for optimal performance. This includes regular cleaning of the electrodes to remove any buildup of contaminants that may affect the accuracy of the measurements. It is also important to store the ph meter properly when not in use to prevent damage to the electrodes.
In conclusion, a ph meter is a valuable tool for measuring the acidity or alkalinity of a solution in various industries. Understanding how a ph meter works is essential for obtaining accurate and reliable results. By following proper calibration and maintenance procedures, users can ensure the accuracy of their measurements and obtain valuable information about the chemical composition of the substances being tested.