Table of Contents
Understanding the Differences Between Regulating Valve and control valve
Regulating Valve vs control valve: Understanding the Differences
When it comes to fluid control systems, valves play a crucial role in regulating the flow of liquids, gases, and other substances. Two common types of valves used in industrial processes are regulating valves and control valves. While these valves may seem similar at first glance, they serve distinct purposes and have specific functions that cater to different needs within a system.
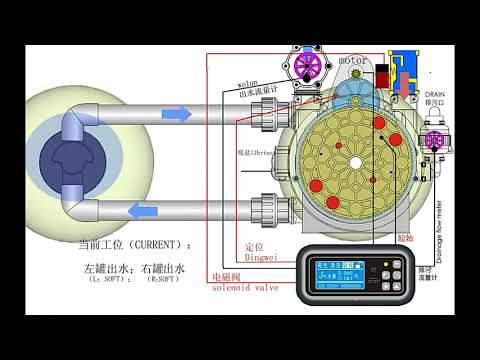
Regulating valves, also known as pressure-reducing valves, are designed to maintain a constant pressure level within a system. These valves work by automatically adjusting the flow of a fluid to ensure that the pressure remains within a specified range. Regulating valves are commonly used in applications where precise pressure control is essential, such as in hydraulic systems, steam boilers, and water supply networks.
On the other hand, control valves are used to regulate the flow rate of a fluid within a system. Unlike regulating valves, control valves are typically operated manually or electronically to adjust the flow of a fluid based on specific requirements. Control valves are often used in processes where flow control is critical, such as in chemical processing plants, oil refineries, and power generation facilities.
One key difference between regulating valves and control valves lies in their primary function. While regulating valves focus on maintaining a constant pressure level, control valves are primarily concerned with regulating the flow rate of a fluid. This distinction is important as it determines the role each type of valve plays in a fluid control system.
Another difference between regulating valves and control valves is their design and operation. Regulating valves are often equipped with a diaphragm or piston mechanism that responds to changes in pressure to adjust the flow of a fluid. In contrast, control valves feature a more complex design that allows for precise control of the flow rate through the use of actuators and positioners.
In terms of applications, regulating valves are commonly used in systems where pressure control is critical to prevent damage or ensure optimal performance. For example, regulating valves are often used in heating and cooling systems to maintain a consistent temperature or in water distribution networks to control water pressure.
Control valves, on the other hand, are versatile valves that can be used in a wide range of applications where flow control is essential. From regulating the flow of chemicals in a manufacturing process to controlling the steam flow in a power plant, control valves play a vital role in ensuring efficient and safe operation of industrial processes.

| Model: Manual Filter Valve | MF2 | MF2-H | MF4 | MF4-B | MF10 |
| Working Position | Filter -> Back wash -> Fast rinse ->Filter | ||||
| Regeneration mode | Manual | ||||
| Inlet | 3/4” | 3/4” | 1” | 1” | 2” |
| Outlet | 3/4” | 3/4” | 1” | 1” | 2” |
| Drain | 3/4” | 3/4” | 1” | 1” | 2” |
| Base | 2-1/2” | 2-1/2” | 2-1/2” | 2-1/2” | 4” |
| Riser pipe | 1.05” OD | 1.05” OD | 1.05” OD | 1.05” OD | 1.5”D-GB |
| Water Capacity | 2m3/h | 2m3/h | 4m3/h | 4m3/h | 10m3/h |
| Working Pressure | 0.15-0.6Mpa | ||||
| Working Temperature | 5-50 °C | ||||
| Power Supply | No need Power | ||||
In conclusion, while regulating valves and control valves both play important roles in fluid control systems, they serve distinct purposes and have specific functions that cater to different needs within a system. Understanding the differences between these two types of valves is essential for selecting the right valve for a particular application and ensuring the optimal performance of a fluid control system.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Regulating Valve and control valve
When it comes to fluid control systems, selecting the right valve is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Two common types of valves used in industrial applications are regulating valves and control valves. While both serve the purpose of controlling the flow of fluids within a system, there are key differences between the two that need to be considered when choosing the most suitable option for a specific application.

Regulating valves are designed to maintain a constant flow rate or pressure within a system. These valves are typically used in applications where precise control over the fluid flow is essential. Regulating valves are often equipped with sophisticated control mechanisms that allow for accurate adjustments to maintain the desired flow rate or pressure levels. These valves are commonly used in processes where maintaining a stable flow is critical, such as in chemical processing plants, refineries, and water treatment facilities.
On the other hand, control valves are more versatile and can be used to regulate not only flow rate and pressure but also other process variables such as temperature, level, and composition. Control valves are often used in systems where dynamic control is required to adjust to changing process conditions. These valves are equipped with actuators that respond to signals from a control system to modulate the flow of fluid based on the setpoint. Control valves are commonly found in industries such as oil and gas, power generation, and pharmaceuticals, where precise control over multiple process variables is necessary.
When deciding between a regulating valve and a control valve, several key factors need to be taken into consideration. The first factor to consider is the level of precision required in controlling the flow of fluid within the system. If maintaining a constant flow rate or pressure is the primary concern, a regulating valve may be the more suitable option. However, if dynamic control over multiple process variables is needed, a control valve would be a better choice.
Another important factor to consider is the type of fluid being controlled and the operating conditions of the system. Regulating valves are often used in applications where the fluid properties remain relatively constant, while control valves are better suited for systems that handle a wide range of fluids with varying properties. Additionally, the operating temperature and pressure of the system can also influence the choice between a regulating valve and a control valve.
| Category | Type | Model | Inlet/Outlet | Drain | Base | Riser Pipe | Brine Line Connector | Water Capacity m3/h |
| automatic softener valve | Downflow Type | ASD2 | 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″ | 1/2″ | 2.5″ | 1.05″ OD | 3/8″ | 2 |
| ASD4 | 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″ | 1/2″ | 2.5″ | 1.05″ OD | 3/8″ | 4 | ||
| ASD10 | 2″ | 1″ | 4″ | 1.5″D-GB | 1/2″ | 10 |
Cost is another factor that needs to be considered when choosing between a regulating valve and a control valve. Regulating valves tend to be more expensive due to their precision control mechanisms, while control valves are more cost-effective for applications that require dynamic control over multiple variables. It is important to weigh the initial cost of the valve against the long-term benefits it provides in terms of system performance and efficiency.
In conclusion, the decision to choose between a regulating valve and a control valve depends on the specific requirements of the fluid control system. By considering factors such as the level of precision needed, the type of fluid being controlled, operating conditions, and cost, engineers can make an informed decision on selecting the most appropriate valve for their application. Ultimately, choosing the right valve is essential for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in fluid control systems.