Table of Contents
Measuring Turbidity: Methods and Best Practices
Turbidity is a key parameter in water quality monitoring, as it provides valuable information about the clarity of water and the presence of suspended particles. High levels of turbidity can indicate pollution, sedimentation, or other contaminants in the water, making it important to regularly test and monitor turbidity levels in bodies of water. In this article, we will discuss the methods and best practices for testing turbidity to ensure accurate and reliable results.
One of the most common methods for measuring turbidity is using a turbidimeter, also known as a nephelometer. This device measures the amount of light scattered by particles in the water, providing a quantitative measurement of turbidity in nephelometric turbidity units (NTU). To use a turbidimeter, simply fill a sample cell with the water to be tested, insert it into the turbidimeter, and take a reading. It is important to calibrate the turbidimeter regularly to ensure accurate results.
Another method for measuring turbidity is the Secchi disk method, which is a simple and cost-effective way to estimate turbidity in bodies of water. To use this method, lower a black and white disk, known as a Secchi disk, into the water until it is no longer visible. The depth at which the disk disappears provides an estimate of turbidity, with deeper depths indicating higher levels of turbidity. While the Secchi disk method is not as precise as using a turbidimeter, it can be a useful tool for quick assessments of water clarity.

In addition to these methods, there are also portable turbidity meters available that provide on-the-spot measurements of turbidity in water samples. These meters are easy to use and provide quick results, making them ideal for field testing and monitoring. When using a portable turbidity meter, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration and operation to ensure accurate readings.
| Product name | PH/ORP-6900 pH/ORP transmitter controller | ||
| Measurement parameter | Measurement Range | Resolution ratio | Accuracy |
| pH | 0.00~14.00 | 0.01 | ±0.1 |
| ORP | (-1999~+1999)mV | 1mV | ±5mV(electric meter) |
| Temperature | (0.0~100.0)℃ | 0.1℃ | ±0.5℃ |
| Temperature range of Tested solution | (0.0~100.0)℃ | ||
| Temperature component | Pt1000 thermal element | ||
| (4~20)mA Current output | Channel No. | 2 Channels | |
| Technical characteristics | Isolated, fully adjustable, reverse, configurable, instrument / transmitting dual mode | ||
| Loop resistance | 400Ω(Max),DC 24V | ||
| Transmission accuracy | ±0.1mA | ||
| Control contact1 | Channel No | 2 Channels | |
| Electric contact | Semiconductor photoelectric switch | ||
| Programmable | Each channel can be programmed and point to (temperature, pH/ORP, time) | ||
| Technical characteristics | Presetting of normally open / normally closed state / pulse /PID regulation | ||
| Load capacity | 50mA(Max)AC/DC 30V | ||
| Control contact2 | Channel No. | 1 Channel | |
| Electric contact | Relay | ||
| Programmable | Each channel can be programmed and point to (temperature, pH/ORP) | ||
| Technical characteristics | Presetting of normally open / normally closed state / pulse /PID regulation | ||
| Load capacity | 3AAC277V / 3A DC30V | ||
| Data communication | RS485, MODBUS standard protocol | ||
| Working power supply | AC220V±10% | ||
| Overall power consumption | <9W | ||
| Working environment | Temperature: (0~50) ℃ Relative humidity: ≤ 85% (non condensing) | ||
| Storage environment | Temperature: (-20~60) C Relative humidity: ≤ 85% (non condensing) | ||
| Protection level | IP65 | ||
| Shape size | 220mm×165mm×60mm (H×W×D) | ||
| Fixed mode | Wall hanging type | ||
| EMC | Level 3 | ||
When testing turbidity, it is important to take multiple measurements at different locations and depths to get a representative sample of the water body. Turbidity levels can vary throughout a body of water, so it is important to test in multiple locations to get an accurate picture of overall water quality. Additionally, it is important to record the date, time, and location of each measurement to track changes in turbidity over time.
To ensure accurate and reliable results when testing turbidity, it is important to follow best practices for sample collection and analysis. When collecting water samples for turbidity testing, be sure to use clean, sterile containers to avoid contamination. It is also important to handle samples carefully to avoid introducing air bubbles, which can affect turbidity measurements. When analyzing samples, be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the specific method or device being used to ensure accurate results.
In conclusion, testing turbidity is an important part of water quality monitoring, as it provides valuable information about the clarity of water and the presence of suspended particles. By using methods such as turbidimeters, Secchi disks, and portable turbidity meters, and following best practices for sample collection and analysis, you can ensure accurate and reliable results when testing turbidity. Regular monitoring of turbidity levels in bodies of water can help identify pollution, sedimentation, or other contaminants, allowing for timely intervention and protection of water resources.
Understanding Turbidity Levels: Importance and Impact on Water Quality
Turbidity is a key parameter used to measure the clarity of water. It refers to the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by suspended particles. These particles can include silt, clay, organic matter, and other debris. Turbidity is an important indicator of water quality as it can affect the health of aquatic ecosystems and the safety of drinking water.
| CCT-3300 | ||||
| Constant | 10.00cm-1 | 1.000cm-1 | 0.100cm-1 | 0.010cm-1 |
| Conductivity | (500~20,000) | (1.0~2,000) | (0.5~200) | (0.05~18.25) |
| μS/cm | μS/cm | μS/cm | MΩ·cm | |
| TDS | (250~10,000) | (0.5~1,000) | (0.25~100) | —— |
| ppm | ppm | ppm | ||
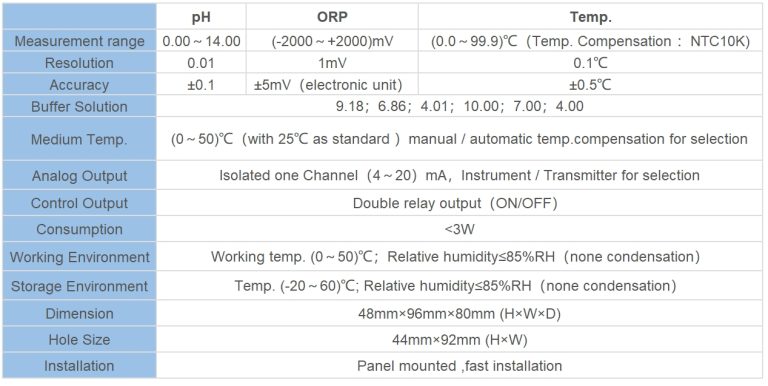
| Medium Temp. | (0~50)℃(Temp. Compensation : NTC10K) | |||
| Resolution | Conductivity: 0.01μS/cm;0.01mS/cm | |||
| TDS: 0.01ppm | ||||
| Temp.: 0.1℃ | ||||
| Accuracy | Conductivity:1.5%(FS) | |||
| Resistivity: 2.0%(FS) | ||||
| TDS:1.5%(FS) | ||||
| Temp:±0.5℃ | ||||
| Analog Output | Single isolated(4~20)mA,instrument/transmitter for selection | |||
| Control Output | SPDT relay,Load Capacity: AC 230V/50A(Max) | |||
| Working Environment | Temp: (0~50)℃;Relative humidity: ≤85%RH(none condensation) | |||
| Storage Environment | Temp:(-20~60)℃; Relative humidity ≤85%RH(none condensation) | |||
| Power Supply | DC 24V/AC 110V/AC 220V±15%(for selection) | |||
| Dimension | 48mm×96mm×80mm (H×W×D) | |||
| Hole Size | 44mm×92mm (H×W) | |||
| Installation | Panel mounted, fast installation | |||
Measuring turbidity is crucial in assessing the overall quality of water sources. High levels of turbidity can indicate the presence of pollutants, pathogens, and other contaminants that may pose a risk to human health and the environment. Therefore, it is essential to regularly monitor turbidity levels in water bodies to ensure that they meet regulatory standards and are safe for consumption.
There are several methods available for testing turbidity, each with its own advantages and limitations. One common method is the use of a turbidimeter, which measures the amount of light scattered by suspended particles in a sample of water. This method is highly accurate and provides real-time results, making it ideal for monitoring turbidity levels in water treatment plants and other facilities.
Another method for testing turbidity is the use of a turbidity tube, which is a simple and cost-effective tool that can be used in the field. The turbidity tube consists of a clear plastic tube with a black and white disk at the bottom. By filling the tube with water and comparing the visibility of the disk, one can estimate the turbidity level of the water sample.

In addition to these methods, there are also portable turbidity meters available that provide quick and reliable measurements of turbidity levels. These meters are easy to use and can be used in the field to assess water quality in real-time. They are particularly useful for monitoring turbidity levels in remote or hard-to-reach areas where access to laboratory equipment may be limited.
When testing turbidity, it is important to follow standard procedures to ensure accurate and consistent results. This includes calibrating equipment, using clean and properly labeled containers for water samples, and following the manufacturer’s instructions for operating the testing equipment. It is also important to record all data accurately and to take multiple measurements to account for any variability in the sample.