Table of Contents
The Importance of Understanding TDS Meter ppm Chart for Water Quality
Water quality is a crucial aspect of our daily lives, as it directly impacts our health and well-being. One of the key indicators of water quality is the Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) level, which measures the concentration of dissolved substances in water. TDS can include a variety of substances such as minerals, salts, metals, and organic matter. Monitoring TDS levels is essential for ensuring that the water we consume is safe and free from harmful contaminants.
One tool that is commonly used to measure TDS levels is a TDS Meter. This device provides a numerical value that represents the concentration of dissolved solids in water, typically measured in parts per million (ppm). Understanding how to interpret the readings from a TDS Meter is crucial for assessing water quality and making informed decisions about water treatment and filtration.
A TDS Meter ppm chart is a valuable resource that provides guidelines for interpreting TDS readings. This chart categorizes TDS levels into different ranges, indicating the quality of water based on the concentration of dissolved solids. By referring to a TDS Meter ppm chart, individuals can determine whether the water they are testing falls within acceptable limits or if further treatment is necessary.

In general, TDS levels below 300 ppm are considered low, indicating that the water is relatively pure and free from contaminants. Water with TDS levels between 300-600 ppm is considered moderate, while levels between 600-900 ppm are considered high. TDS levels above 900 ppm are considered very high and may indicate the presence of harmful substances that could pose health risks.
It is important to note that TDS levels alone do not provide a complete picture of water quality. While high TDS levels can indicate the presence of contaminants, low TDS levels do not necessarily guarantee that the water is safe to drink. Other factors such as pH, turbidity, and specific contaminants should also be considered when assessing water quality.
By using a TDS Meter ppm chart in conjunction with other water quality tests, individuals can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the overall health and safety of their water supply. Regular monitoring of TDS levels can help identify changes in water quality over time and prompt the need for corrective action if necessary.
In addition to monitoring TDS levels in drinking water, TDS meters can also be used to assess the quality of water in aquariums, pools, and hydroponic systems. By maintaining appropriate TDS levels in these environments, individuals can ensure the health and well-being of aquatic plants and animals.
In conclusion, understanding how to interpret TDS readings using a TDS Meter ppm chart is essential for assessing water quality and making informed decisions about water treatment. By monitoring TDS levels regularly and taking appropriate action when necessary, individuals can help ensure that the water they consume is safe and free from harmful contaminants. Investing in a TDS Meter and familiarizing oneself with a TDS Meter ppm chart is a proactive step towards safeguarding the health and well-being of oneself and others.
How to Use TDS Meter ppm Chart to Monitor and Maintain Water Quality
A TDS Meter is a valuable tool for monitoring and maintaining water quality. Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) refer to the amount of inorganic and organic substances that are dissolved in water. These substances can include minerals, salts, metals, and other compounds. Measuring TDS levels can help determine the overall quality of water and identify any potential issues that may need to be addressed.
One way to interpret TDS levels is by using a TDS Meter ppm chart. PPM stands for parts per million, which is a unit of measurement used to express the concentration of a substance in water. The TDS Meter ppm chart provides a range of values that correspond to different levels of TDS in water. By comparing the TDS reading from the meter to the values on the chart, you can determine whether the water is within an acceptable range or if further action is needed.
For example, a TDS reading of 0-50 PPM is considered very low and may indicate that the water is lacking essential minerals. On the other hand, a reading of 1000 PPM or higher is considered very high and may indicate the presence of contaminants or pollutants. By using the TDS Meter ppm chart, you can quickly assess the quality of water and take appropriate measures to address any issues that may arise.
It is important to note that TDS levels can vary depending on the source of water. For example, tap water may have higher TDS levels due to the presence of minerals and additives used in the treatment process. On the other hand, well water may have lower TDS levels if it has not been treated with chemicals or additives. By regularly monitoring TDS levels and referring to the TDS Meter ppm chart, you can track changes in water quality over time and make informed decisions about how to maintain or improve it.
In addition to using the TDS Meter ppm chart, there are other factors to consider when monitoring water quality. pH levels, temperature, and turbidity can all impact the overall quality of water. By taking a comprehensive approach to water testing and monitoring, you can ensure that your water is safe for consumption and other uses.
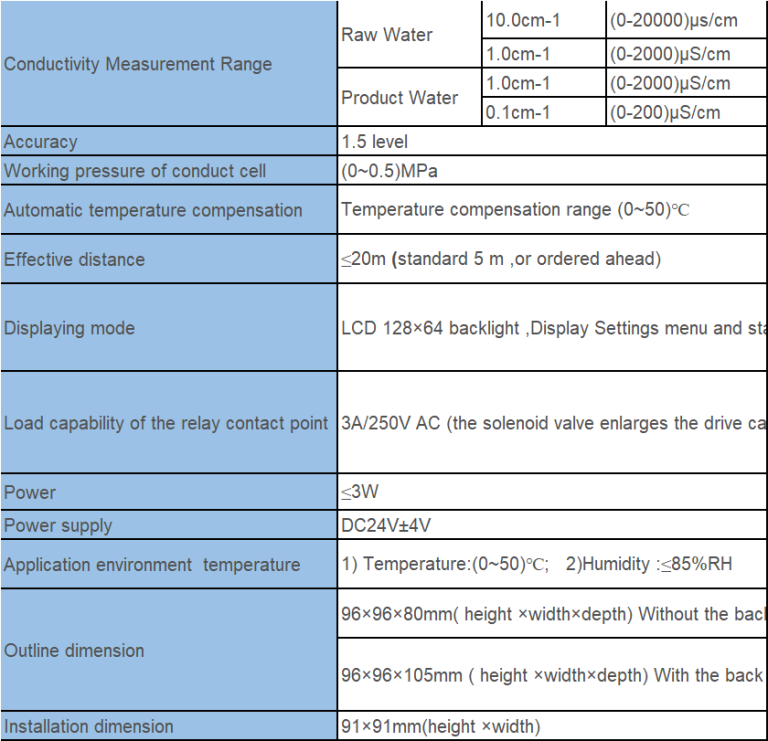
| Model No. | CIT-8800 Inductive Conductivity / Concentration Online Controller | |
| Measurement range | Conductivity | 0.00\u03bcS/cm ~ 2000mS/cm |
| Concentration | 1.NaOH\uff0c\uff080-15\uff09% or\uff0825-50\uff09%\uff1b | |
| 2.HNO3\uff08note the Corrosion resistance of the sensor\uff09\uff080-25\uff09% or\uff0836-82\uff09%\uff1b | ||
| 3.User-defined concentration curves. | ||
| TDS | 0.00ppm~1000ppt | |
| Temp. | \uff080.0 ~ 120.0\uff09\u2103 | |
| Resolution | Conductivity | 0.01\u03bcS/cm |
| Concentration | 0.01% | |
| TDS | 0.01ppm | |
| Temp. | 0.1\u2103 | |
| Accuracy | Conductivity | 0\u03bcS/cm ~1000\u03bcS/cm \u00b110\u03bcS/cm |
| 1 mS/cm~500 mS/cm \u00b11.0% | ||
| 500mS/cm~2000 mS/cm \u00b11.0% | ||
| TDS | 1.5 level | |
| Temp. | \u00b10.5\u2103 | |
| Temp. compensation | element | Pt1000 |
| range | \uff080.0~120.0\uff09\u2103 linear compensation | |
| \uff084~20\uff09mA Current output | channels | Double channels |
| features | Isolated, adjustable, reversible, 4-20MA output, instruments/ transmitter mode. | |
| Loop resistance | 400\u03a9\uff08Max\uff09\uff0cDC 24V | |
| Resolution | \u00b10.1mA | |
| Control contact | Channels | Triple channels |
| Contact | Photoelectric relay output | |
| Programmable | Programmable \uff08 temperature \u3001conductivity/concentration/TDS\u3001timing\uff09output | |
| Features | Could set temperature\u3001conductivity/concentration/TDS\u3001 timing NO/NC/ PID selection | |
| Resistance load | 50mA\uff08Max\uff09\uff0cAC/DC 30V\uff08Max\uff09 | |
| Data communication | RS485,MODBUS protocol | |
| Power supply | DC 24V\u00b14V | |
| Consumption | \uff1c5.5W | |
| Working environment | Temperature\uff1a\uff080~50\uff09\u2103 Relative Humidity\uff1a\u226485%RH(non- condensing ) | |
| Storage | Temperature\uff1a(-20~60)\u2103 Relative Humidity\uff1a\u226485%RH(non- condensing) | |
| Protection level | IP65\uff08with rear cover\uff09 | |
| Outline dimension | 96mm\u00d796 mm\u00d794mm (H\u00d7W\u00d7D) | |
| Hole dimension | 91mm\u00d791mm(H\u00d7W) | |
| Installation | Panel mounted , fast installation | |
In conclusion, a TDS Meter ppm chart is a valuable tool for monitoring and maintaining water quality. By comparing TDS readings to the values on the chart, you can quickly assess the quality of water and identify any potential issues that may need to be addressed. By taking a comprehensive approach to water testing and monitoring, you can ensure that your water is safe for consumption and other uses. Remember to regularly test your water and refer to the TDS Meter ppm chart to keep track of changes in water quality over time.