Table of Contents
The Importance of Monitoring Water Quality with TDS Meters
Water quality is a critical aspect of our daily lives, as it directly impacts our health and well-being. One of the key parameters used to assess water quality is total dissolved solids (TDS). TDS refers to the total amount of inorganic and organic substances dissolved in water, including minerals, salts, metals, and other compounds. Monitoring TDS levels in water is essential to ensure that it is safe for consumption and other uses.
There are several methods available for measuring TDS levels in water, with two common options being TDS meters and hardness strips. TDS meters are electronic devices that measure the electrical conductivity of water to determine TDS levels, while hardness strips use chemical reactions to estimate TDS levels based on the water’s hardness. Both methods have their advantages and limitations, making it important to understand the differences between them.
TDS meters are widely used in water quality testing due to their accuracy and ease of use. These devices provide precise measurements of TDS levels in water, allowing users to quickly assess the water’s quality. TDS meters are also versatile, as they can be used to test a wide range of water sources, including tap water, well water, and even aquarium water. Additionally, TDS meters are relatively affordable and require minimal maintenance, making them a cost-effective option for monitoring water quality.
On the other hand, hardness strips are a more traditional method of measuring TDS levels in water. These strips contain chemical reagents that react with the minerals and salts in water, producing a color change that indicates the water’s hardness. While hardness strips are easy to use and do not require any special equipment, they are less accurate than TDS meters. Hardness strips may also be less reliable for testing water with high TDS levels or complex compositions, as the chemical reactions may not accurately reflect the true TDS levels.
When choosing between TDS meters and hardness strips for monitoring water quality, it is important to consider the specific needs and requirements of the application. TDS meters are ideal for users who require precise and reliable measurements of TDS levels in water, such as in laboratory settings or for commercial water treatment systems. Hardness strips, on the other hand, may be suitable for general water quality testing or for users who prefer a simpler and more affordable option.
In conclusion, monitoring TDS levels in water is essential for ensuring its safety and quality. TDS meters and hardness strips are two common methods for measuring TDS levels, each with its own advantages and limitations. While TDS meters offer accurate and reliable measurements, hardness strips provide a simpler and more affordable option for general water quality testing. Ultimately, the choice between TDS meters and hardness strips will depend on the specific needs and preferences of the user. Regardless of the method chosen, regular monitoring of TDS levels in water is crucial for maintaining clean and safe water for consumption and other uses.
Pros and Cons of Using Hardness Strips for Water Testing
When it comes to testing the quality of water, there are various methods available to consumers. Two popular options for testing water hardness are using a TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) meter or hardness strips. Both methods have their own set of pros and cons, which we will explore in this article.
Hardness strips are a simple and cost-effective way to test water hardness. They typically come in a pack of strips that change color when dipped into water. The color change corresponds to the level of hardness in the water, making it easy for consumers to interpret the results. Hardness strips are convenient to use and provide quick results, making them a popular choice for homeowners looking to test their water quality.

One of the main advantages of using hardness strips is their affordability. They are relatively inexpensive compared to other testing methods, making them accessible to a wide range of consumers. Additionally, hardness strips are easy to use and do not require any special equipment or training. This makes them a convenient option for homeowners who want to quickly test their water quality without any hassle.
However, there are some drawbacks to using hardness strips for water testing. One of the main limitations is their accuracy. Hardness strips provide a general indication of water hardness, but they may not be as precise as other testing methods. This can lead to inaccurate results, which may not give consumers a complete picture of their water quality.
Another disadvantage of hardness strips is their limited range of testing. Most hardness strips are designed to test for a specific range of hardness levels, which may not cover the full spectrum of water hardness. This can be a problem for consumers who want to know the exact hardness level of their water.
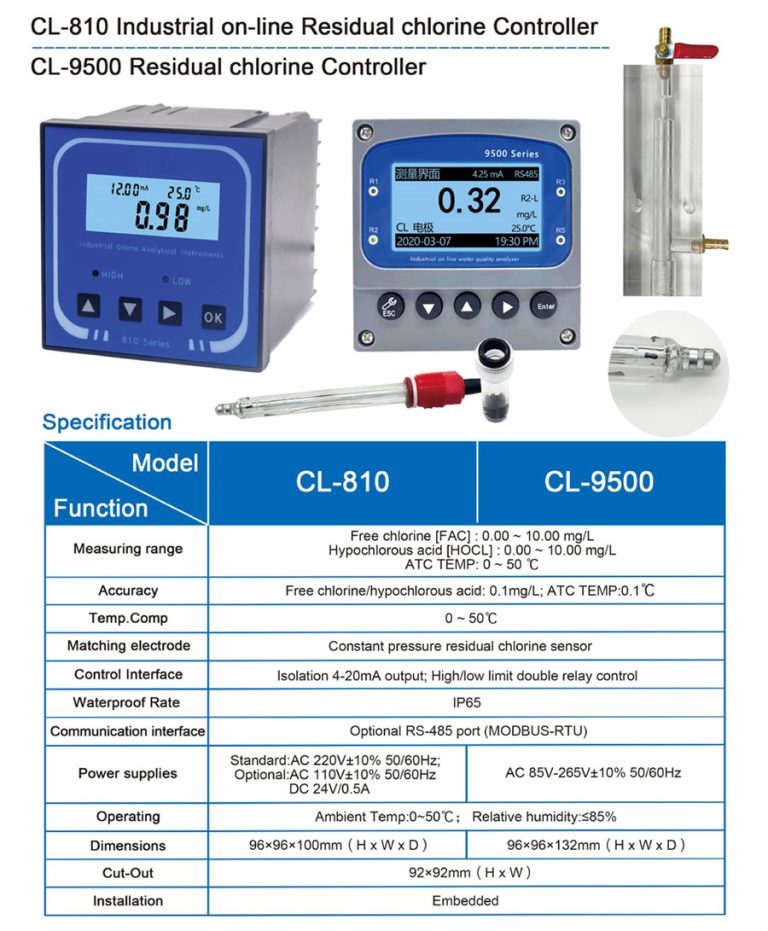
| Model | CL-810/9500 Residual Chlorine Controller |
| Range | FAC/HOCL:0-10 mg/L, ATC TEMP:0-50℃ |
| Accuracy | FAC/HOCL:0.1 mg/L, ATC TEMP:0.1℃ |
| Oper. Temp. | 0~50℃ |
| Sensor | Constant Pressure Residual Chlorine Sensor |
| Waterproof Rate | IP65 |
| Communication | Optional RS485 |
| Output | 4-20mA output; High/Low limit double relay control |
| Power | CL-810:AC 220V±10% 50/60Hz or AC 110V±10% 50/60Hz or DC24V/0.5A |
| CL-9500:AC 85V-265V±10% 50/60Hz | |
| Working Environment | Ambient temperature:0~50℃; |
| Relative humidity≤85% | |
| Dimensions | CL-810:96×96×100mm(H×W×L) |
| CL-9500:96×96×132mm(H×W×L) | |
| Hole Size | 92×92mm(H×W) |
| Installation Mode | Embedded |
On the other hand, TDS meters offer a more precise and comprehensive way to test water quality. These devices measure the total dissolved solids in water, which includes minerals, salts, and other substances. TDS meters provide a numerical value that indicates the overall quality of the water, giving consumers a more detailed analysis of their water hardness.
One of the main advantages of using a TDS Meter is its accuracy. These devices provide precise measurements of water quality, giving consumers a more reliable indication of their water hardness. TDS meters are also versatile and can be used to test a wide range of water sources, making them a valuable tool for homeowners who want to monitor their water quality over time.
However, there are some drawbacks to using a TDS Meter for water testing. One of the main limitations is their cost. TDS meters are more expensive than hardness strips, which may deter some consumers from investing in this type of testing method. Additionally, TDS meters require calibration and maintenance to ensure accurate results, which can be a hassle for some users.
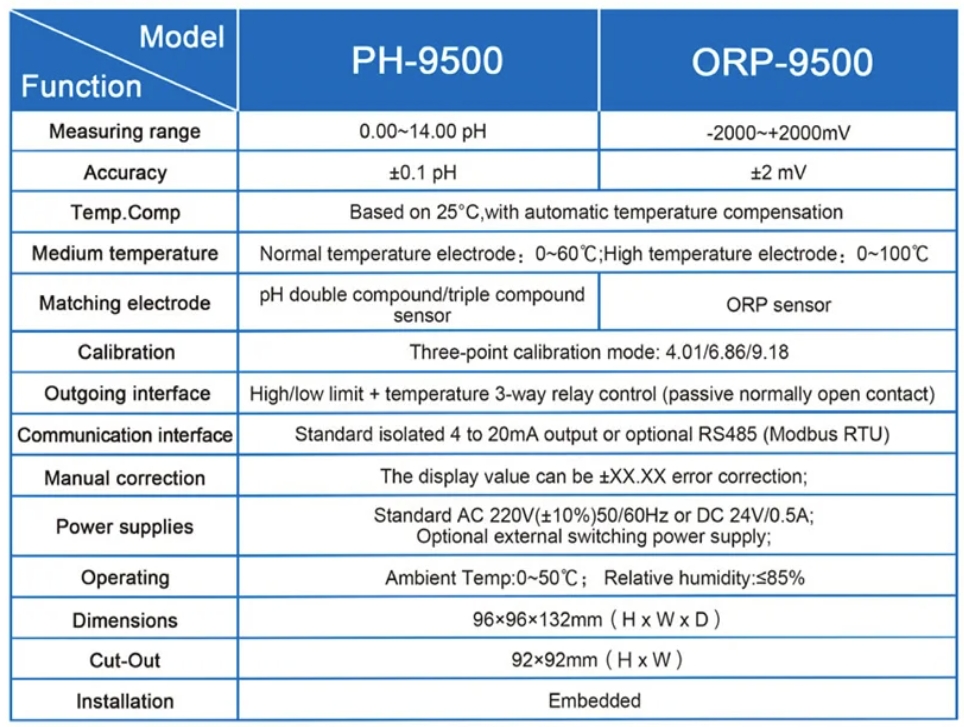
| Model | pH/ORP-9500 pH/orp meter |
| Range | 0-14 pH; -2000 – +2000mV |
| Accuracy | ±0.1pH; ±2mV |
| Temp. Comp. | Automatic temperature compensation |
| Oper. Temp. | Normal 0~50℃; High temp 0~100℃ |
| Sensor | pH double/triple sensor; ORP sensor |
| Display | LCD Screen |
| Communication | 4-20mA output/RS485 |
| Output | High/Low limit triple relay control |
| Power | AC 220V±10% 50/60Hz or AC 110V±10% 50/60Hz or DC24V/0.5A |
| Working Environment | Ambient temperature:0~50℃ |
| Relative humidity≤85% | |
| Dimensions | 96×96×132mm(H×W×L) |
| Hole Size | 92×92mm(H×W) |
| Installation Mode | Embedded |
In conclusion, both hardness strips and TDS meters have their own set of pros and cons when it comes to testing water hardness. Hardness strips are affordable and convenient, but may not provide the most accurate results. TDS meters offer precise measurements and comprehensive analysis, but come with a higher cost and maintenance requirements. Ultimately, the choice between these two methods will depend on the individual needs and preferences of the consumer.