Table of Contents
Benefits of Using a digital conductivity meter
Conductivity meters are essential tools used in various industries to measure the ability of a solution to conduct electricity. They are commonly used in water treatment plants, laboratories, and manufacturing facilities to ensure the quality and consistency of products. There are different types of conductivity meters available on the market, each with its own unique features and benefits.
One of the most popular types of conductivity meters is the digital conductivity meter. Digital conductivity meters are highly accurate and easy to use, making them ideal for a wide range of applications. These meters use advanced technology to provide precise measurements of conductivity, making them a valuable tool for quality control and process monitoring.
One of the key benefits of using a digital conductivity meter is its accuracy. Digital meters are designed to provide precise measurements of conductivity, ensuring that the results are reliable and consistent. This level of accuracy is essential in industries where even small variations in conductivity can have a significant impact on the quality of the final product.

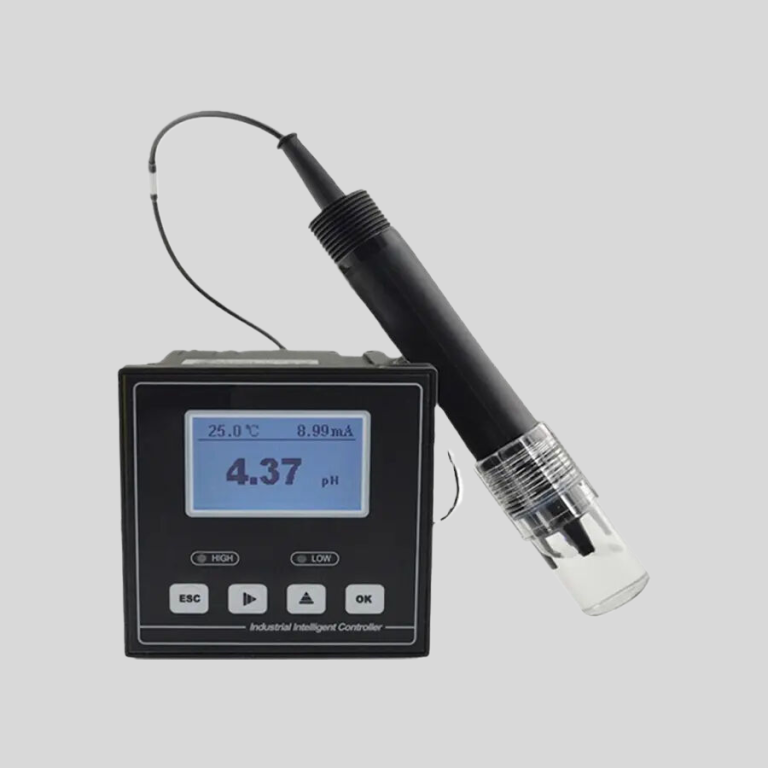
In addition to accuracy, digital conductivity meters are also known for their ease of use. These meters are typically equipped with user-friendly interfaces and intuitive controls, making them easy to operate even for those with limited technical knowledge. This ease of use allows operators to quickly and efficiently measure conductivity without the need for extensive training or experience.
Another benefit of digital conductivity meters is their versatility. These meters are capable of measuring a wide range of conductivity levels, making them suitable for a variety of applications. Whether you need to measure low conductivity levels in pure water or high conductivity levels in a concentrated solution, a digital conductivity meter can provide accurate and reliable results.
| Model | EC-510 Intelligent conductivity meter |
| Range | 0-200/2000/4000/10000uS/cm |
| 0-18.25M\u03a9 | |
| Accuracy | 1.5%(FS) |
| Temp. Comp. | Automatic temperature compensation |
| Oper. Temp. | Normal 0\uff5e50\u2103; High temp 0\uff5e120\u2103 |
| Sensor | C=0.01/0.02/0.1/1.0/10.0cm-1 |
| Display | LCD Screen |
| Communication | 4-20mA output/2-10V/1-5V/RS485 |
| Output | High/Low limit dual relay control |
| Power | AC 220V\u00b110% 50/60Hz or AC 110V\u00b110% 50/60Hz or DC24V/0.5A |
| Working Environment | Ambient temperature:0\uff5e50\u2103 |
| Relative humidity\u226485% | |
| Dimensions | 48\u00d796\u00d7100mm(H\u00d7W\u00d7L) |
| Hole Size | 45\u00d792mm(H\u00d7W) |
| Installation Mode | Embedded |
Digital conductivity meters also offer the advantage of real-time monitoring. Many digital meters are equipped with built-in data logging capabilities, allowing operators to track conductivity levels over time. This real-time monitoring is essential for identifying trends and detecting any changes in conductivity that may indicate a problem or deviation from the desired specifications.
Furthermore, digital conductivity meters are often more durable and reliable than traditional analog meters. Digital meters are less susceptible to drift and calibration issues, ensuring that the measurements remain accurate and consistent over time. This reliability is crucial in industries where precise control of conductivity is essential for maintaining product quality and meeting regulatory requirements.
Overall, the benefits of using a digital conductivity meter are clear. These meters offer unparalleled accuracy, ease of use, versatility, real-time monitoring, and reliability, making them an indispensable tool for industries that rely on precise measurements of conductivity. Whether you are working in a water treatment plant, a laboratory, or a manufacturing facility, a digital conductivity meter can help you ensure the quality and consistency of your products.
Comparison of Benchtop vs. Portable Conductivity Meters
Conductivity meters are essential tools used in various industries to measure the ability of a solution to conduct electricity. They are commonly used in laboratories, water treatment plants, and manufacturing facilities to monitor the quality of water, chemicals, and other liquids. There are two main types of conductivity meters: benchtop and portable. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications.
Benchtop conductivity meters are larger, more sophisticated instruments that are typically used in laboratory settings where accuracy and precision are crucial. These meters are designed to provide highly accurate measurements and are often equipped with advanced features such as temperature compensation and data logging capabilities. Benchtop conductivity meters are ideal for applications that require precise measurements and where portability is not a concern.
One of the main differences between benchtop and portable conductivity meters is their size and portability. Benchtop meters are larger and heavier, making them less convenient for fieldwork. Portable meters, on the other hand, are compact and lightweight, allowing users to easily carry them from one location to another. This makes portable meters more suitable for applications that require measurements to be taken in different locations.
Another difference between benchtop and portable conductivity meters is their level of accuracy. Benchtop meters are typically more accurate and precise than portable meters, making them ideal for applications that require high levels of accuracy. Portable meters, while less accurate, are still suitable for many applications where precision is not critical.
In terms of cost, benchtop conductivity meters are generally more expensive than portable meters. This is due to the advanced features and higher level of accuracy that benchtop meters offer. Portable meters, while less expensive, still provide reliable measurements at a lower cost.
When choosing between benchtop and portable conductivity meters, it is important to consider the specific requirements of the application. If accuracy and precision are paramount, a benchtop meter may be the best choice. However, if portability and convenience are more important, a portable meter may be the better option.
In conclusion, both benchtop and portable conductivity meters have their own advantages and disadvantages. Benchtop meters are ideal for applications that require high levels of accuracy and precision, while portable meters are more suitable for fieldwork and on-the-go measurements. Ultimately, the choice between the two types of meters will depend on the specific requirements of the application and the user’s preferences.