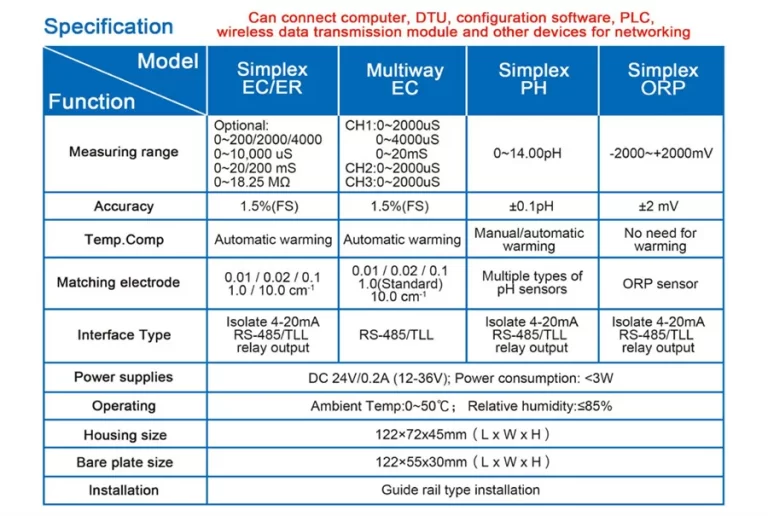
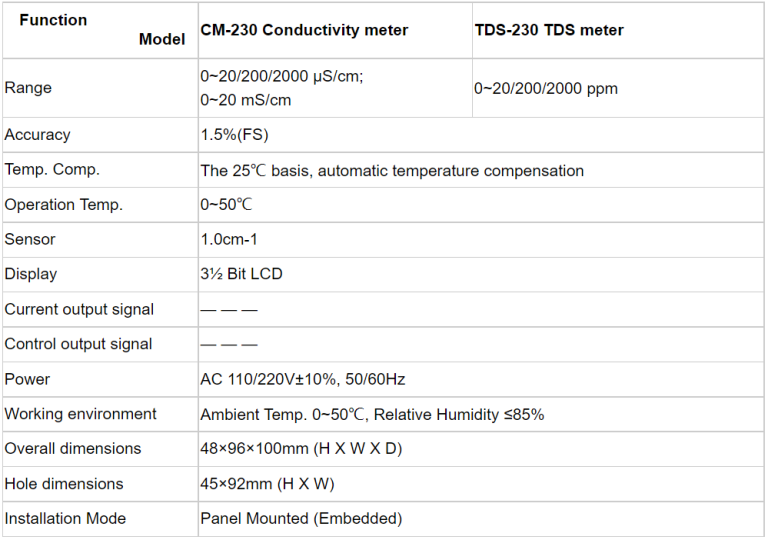
Table of Contents
Benefits of Using Water Quality Testing Images in Environmental Monitoring
Water quality testing is a crucial aspect of environmental monitoring, as it helps to ensure the safety of our water sources and protect the health of both humans and ecosystems. In recent years, advancements in technology have made it easier than ever to collect and analyze water quality data. One such advancement is the use of water quality testing images, which provide a visual representation of water quality parameters and can help to identify potential issues more quickly and accurately.

Additionally, water quality testing images can help to detect changes in water quality more quickly than traditional testing methods. By capturing images of water samples at regular intervals, researchers can track changes in parameters such as turbidity, algae levels, or nutrient concentrations over time. This can help to identify potential sources of pollution or other issues before they become more serious, allowing for more timely intervention and mitigation efforts.
| Model | CL-810/9500 Residual Chlorine Controller |
| Range | FAC/HOCL:0-10 mg/L, ATC TEMP:0-50\u2103 |
| Accuracy | FAC/HOCL:0.1 mg/L, ATC TEMP:0.1\u2103 |
| Oper. Temp. | 0\uff5e50\u2103 |
| Sensor | Constant Pressure Residual Chlorine Sensor |
| Waterproof Rate | IP65 |
| Communication | Optional RS485 |
| Output | 4-20mA output; High/Low limit double relay control |
| Power | CL-810:AC 220V\u00b110% 50/60Hz or AC 110V\u00b110% 50/60Hz or DC24V/0.5A |
| CL-9500:AC 85V-265V\u00b110% 50/60Hz | |
| Working Environment | Ambient temperature:0\uff5e50\u2103; |
| Relative humidity\u226485% | |
| Dimensions | CL-810:96\u00d796\u00d7100mm(H\u00d7W\u00d7L) |
| CL-9500:96\u00d796\u00d7132mm(H\u00d7W\u00d7L) | |
| Hole Size | 92\u00d792mm(H\u00d7W) |
| Installation Mode | Embedded |
Another benefit of using water quality testing images is that they can help to improve data accuracy and reliability. Traditional water quality tests can be subject to human error or bias, leading to inaccurate results. By using imaging technology to capture and analyze water quality data, researchers can reduce the risk of errors and ensure that their findings are more reliable. This can help to build trust in the data and make it more useful for decision-making and policy development.
Furthermore, water quality testing images can help to enhance public awareness and engagement around water quality issues. By providing visual representations of water quality data, researchers can make their findings more accessible and understandable to a wider audience. This can help to raise awareness about the importance of water quality monitoring and encourage individuals and communities to take action to protect their local water sources.
In conclusion, water quality testing images offer a range of benefits for environmental monitoring efforts. From providing a more comprehensive view of water quality to detecting changes more quickly and accurately, imaging technology can help to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of water quality testing. By leveraging the power of visual data, researchers can enhance their understanding of water quality issues and empower communities to take action to protect their water sources. As technology continues to advance, water quality testing images are likely to play an increasingly important role in safeguarding our water resources for future generations.
How to Interpret Water Quality Testing Images for Improved Analysis and Reporting
Water quality testing is a crucial aspect of ensuring the safety and health of our water supply. By analyzing water quality testing images, researchers and scientists can gain valuable insights into the presence of contaminants and pollutants in water sources. Interpreting these images accurately is essential for making informed decisions about water treatment and management strategies.
When interpreting water quality testing images, it is important to consider the various parameters being measured, such as pH, turbidity, dissolved oxygen, and levels of specific contaminants like heavy metals or bacteria. Each parameter provides valuable information about the overall quality of the water and can help identify potential sources of pollution or contamination.
One of the key factors to consider when interpreting water quality testing images is the color and clarity of the water sample. Cloudy or discolored water can indicate the presence of suspended solids or organic matter, which can affect the overall quality of the water. By analyzing the color and clarity of the water sample, researchers can gain insights into the potential sources of pollution and develop strategies to address these issues.
Another important parameter to consider when interpreting water quality testing images is the presence of specific contaminants or pollutants. Images that show high levels of contaminants like heavy metals or bacteria can indicate potential health risks associated with the water source. By identifying these contaminants early on, researchers can take proactive measures to mitigate their impact and protect public health.
In addition to analyzing specific contaminants, researchers should also pay attention to the overall composition of the water sample. For example, high levels of dissolved oxygen can indicate a healthy ecosystem, while low levels may suggest pollution or other environmental stressors. By analyzing the composition of the water sample, researchers can gain insights into the overall health of the water source and develop strategies to improve water quality.
Transitional phrases such as “in addition,” “furthermore,” and “on the other hand” can help guide the reader through the interpretation process and connect different ideas and concepts. By using these transitional phrases effectively, researchers can ensure that their analysis is clear, concise, and easy to follow.
Overall, interpreting water quality testing images is a complex process that requires careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the various parameters being measured. By analyzing the color, clarity, composition, and presence of specific contaminants in water samples, researchers can gain valuable insights into the overall quality of the water source and develop strategies to improve water quality and protect public health. By using transitional phrases to guide the reader through the interpretation process, researchers can ensure that their analysis is clear, concise, and easy to follow, ultimately leading to improved analysis and reporting of water quality testing images.