Understanding the Basic Principle of Conductivity Meters
Conductivity meters are essential tools used in various industries to measure the ability of a solution to conduct electricity. Understanding the basic principle of conductivity meters is crucial for their proper use and accurate readings. In this article, we will delve into the fundamental principles behind conductivity meters and how they work.
At its core, conductivity is a measure of how well a solution can conduct electricity. The conductivity of a solution is determined by the presence of ions, which are charged particles that allow the flow of electricity. In general, the higher the concentration of ions in a solution, the higher its conductivity.

Conductivity meters work by measuring the electrical conductivity of a solution. The basic principle behind conductivity meters is to pass an electrical current through the solution and measure the resulting voltage. The conductivity of the solution is then calculated based on the relationship between the current, voltage, and the distance between the electrodes.
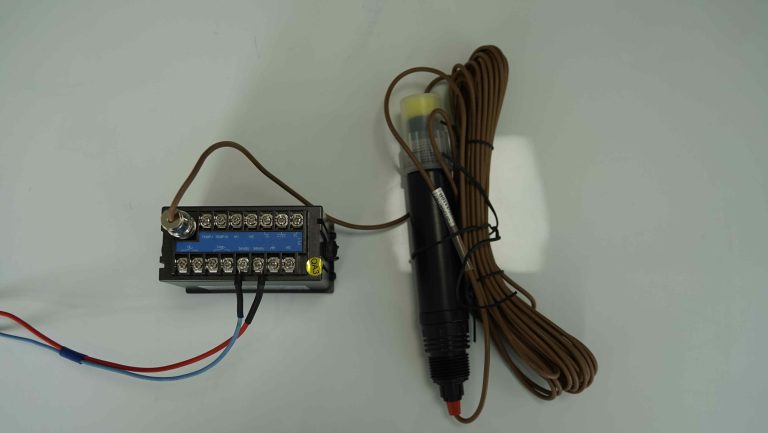
The key components of a conductivity meter include electrodes, a power source, and a measuring circuit. The electrodes are immersed in the solution being tested and are responsible for passing the electrical current through the solution. The power source provides the necessary electrical energy to generate the current, while the measuring circuit measures the voltage across the electrodes.
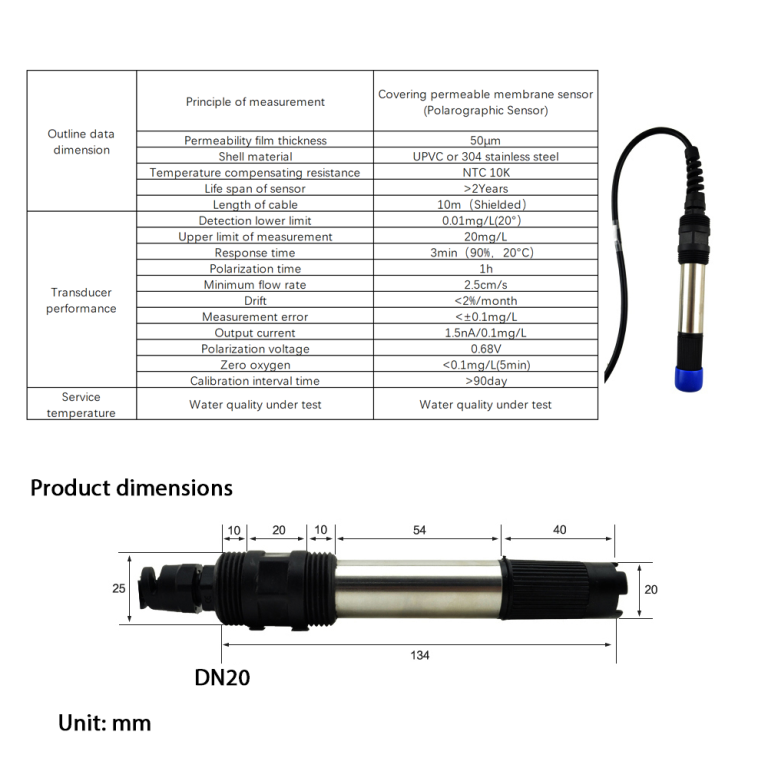
| Product Model | DOF-6310 (DOF-6141) |
| Product Name | Dissolved oxygen data collection terminal |
| Measuring Method | Fluorescence Method |
| Measurement range | 0-20mg/L |
| Accuracy | ±0.3mg/L |
| Resolution | 0.01mg/L |
| Response time | 90s |
| Repeatibility | 5%RS |
| Temperature compensation | 0-60.0℃ Accuracy:±0.5℃ |
| Air pressure compensation | 300-1100hPa |
| Stand pressure | 0.3Mpa |
| Communication | RS485 MODBUS-RTU standard protocol |
| Power | DC(9-28)V |
| Power comsuption | <2W |
| Operational envrionment | Temperature:(0-50)℃ |
| Storage Environment | Temperature:(-10-60)℃; Humidity:≤95%RH(None condensation) |
| Installation | Submerged |
| Protection Level | IP68 |
| Weight | 1.5Kg(with 10m cable) |
When the electrodes are immersed in a solution, the ions present in the solution allow the flow of electricity between the electrodes. The conductivity meter measures the voltage drop across the electrodes, which is directly proportional to the conductivity of the solution. By measuring the voltage drop and knowing the current passing through the solution, the conductivity of the solution can be accurately calculated.
It is important to note that conductivity meters are calibrated using standard solutions with known conductivity values. This calibration process ensures the accuracy and reliability of the conductivity meter readings. By comparing the measured conductivity of a solution to the known conductivity of the standard solutions, the accuracy of the conductivity meter can be verified.
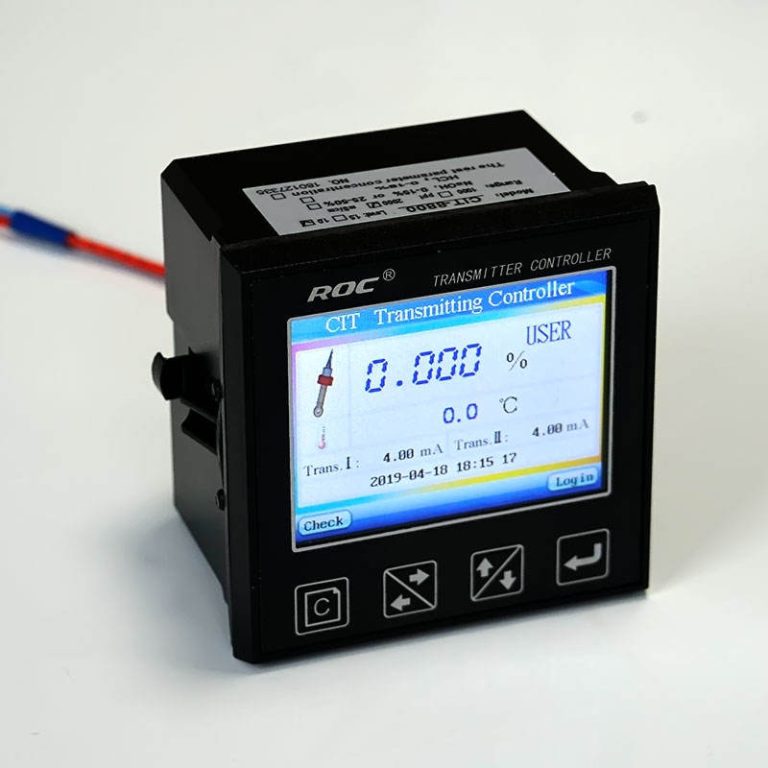
Conductivity meters are widely used in various industries, including water treatment, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and food and beverage production. In water treatment plants, conductivity meters are used to monitor the quality of water and ensure that it meets regulatory standards. In pharmaceuticals, conductivity meters are used to measure the purity of drug formulations. In agriculture, conductivity meters are used to monitor soil salinity levels. In food and beverage production, conductivity meters are used to ensure the quality and consistency of products.
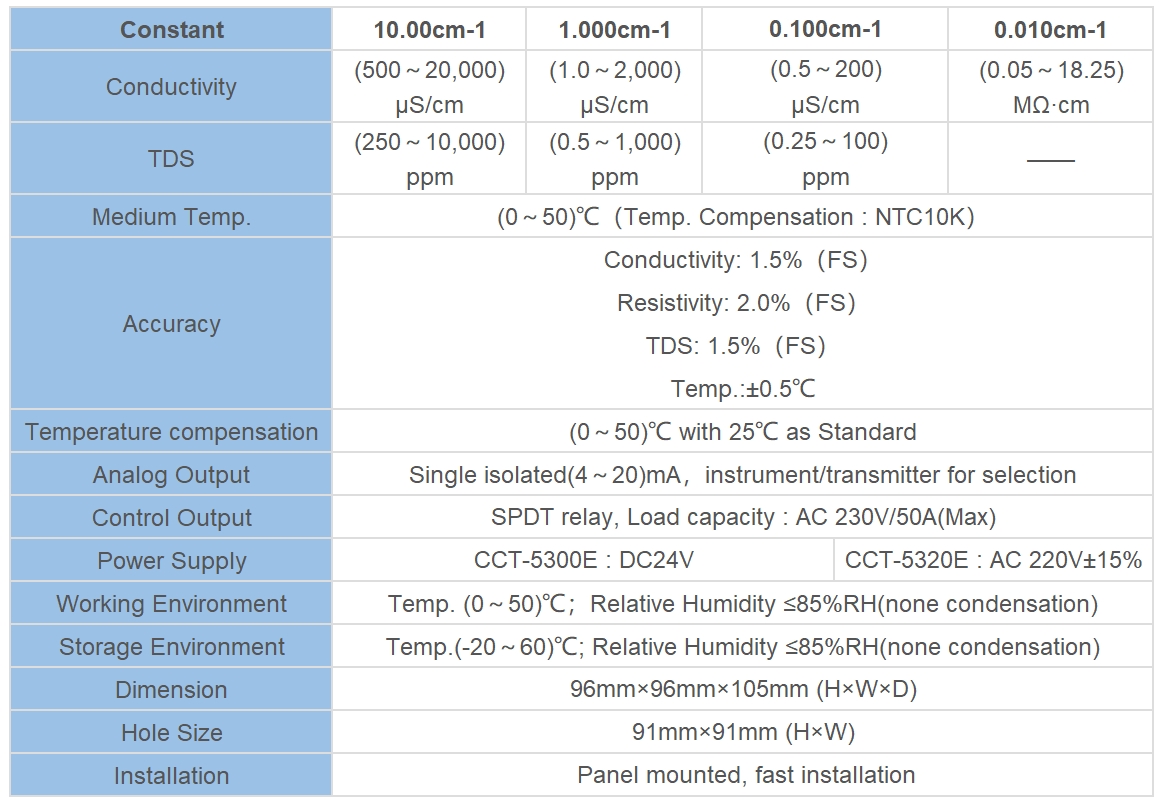
| Model | ROC-8221 Single Stage Double Channels ro controller | ||
| Conductivity Measurement Range | Raw Water | 10.0cm-1 | (0-20000)μs/cm |
| 1.0cm-1 | (0-2000)μS/cm | ||
| Product Water | 1.0cm-1 | (0-2000)μS/cm | |
| 0.1cm-1 | (0-200)μS/cm | ||
| Accuracy | 1.5 level | ||
| Working pressure of conduct cell | (0~0.5)MPa | ||
| Automatic temperature compensation | Temperature compensation range (0~50)℃ | ||
| Effective distance | ≤20m (standard 5 m ,or ordered ahead) | ||
| Displaying mode | LCD 128×64 backlight ,Display Settings menu and status message in English or Chinese can be selection | ||






