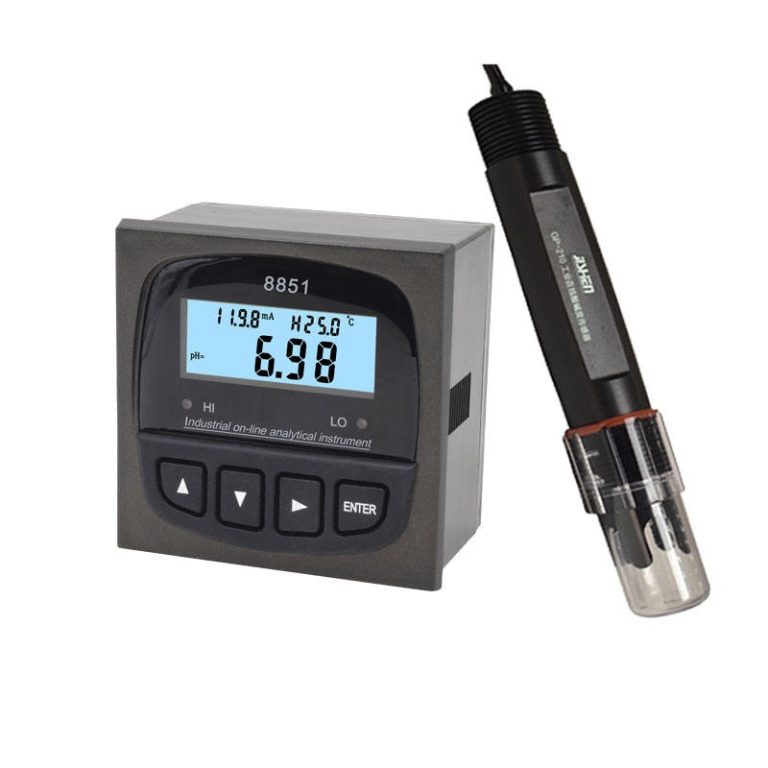
Potentiometer is also called as ph meter because it measures the potential difference between two electrodes to determine the acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
The Relationship Between Potentiometer and ph meter
Potentiometers and pH meters are two devices that are commonly used in various fields, such as chemistry, biology, and environmental science. While they may seem like two completely different instruments, there is actually a close relationship between the two. In fact, potentiometers are often referred to as pH meters due to their ability to measure pH levels accurately.

On the other hand, a ph meter is a device used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It does this by measuring the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution, which is expressed as the pH level. The ph meter consists of a glass electrode that is sensitive to changes in hydrogen ion concentration and a reference electrode that provides a stable voltage. By measuring the voltage difference between the two electrodes, the ph meter can determine the pH level of the solution.
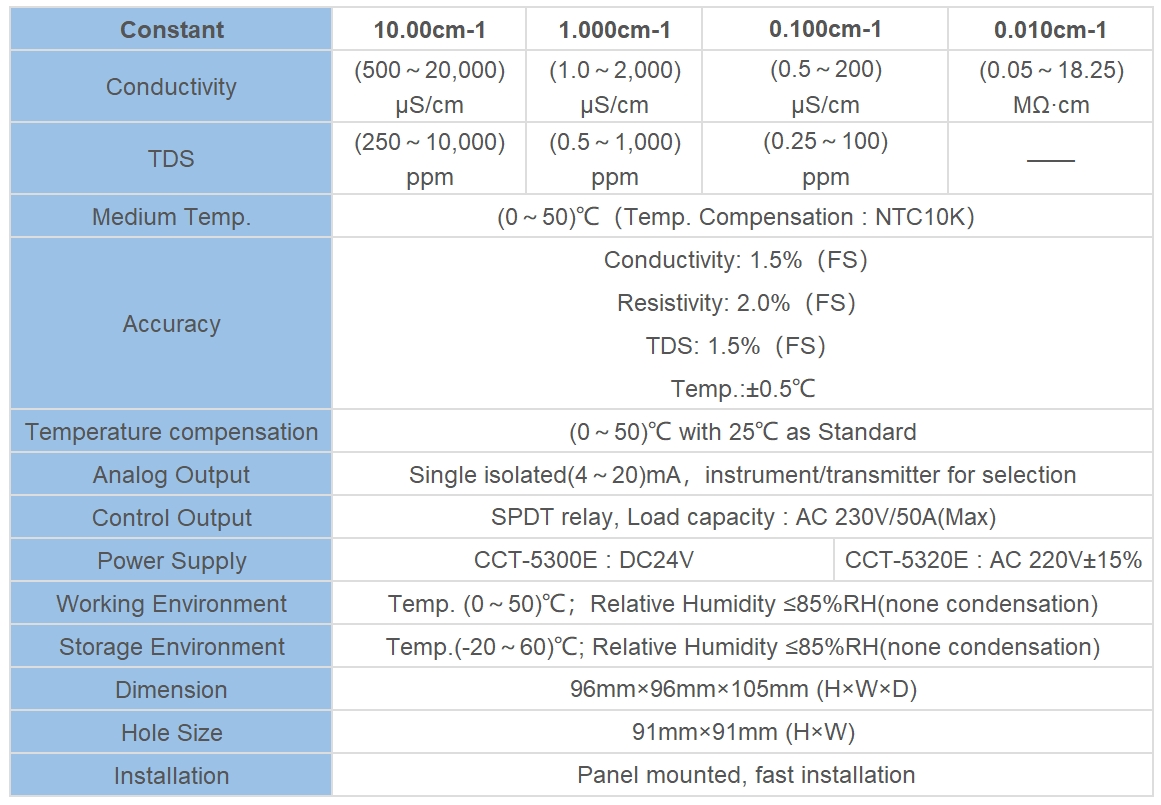
The relationship between potentiometers and pH meters lies in the fact that both devices rely on measuring voltage differences to provide accurate measurements. In the case of a ph meter, the voltage difference is used to determine the pH level of a solution, while in a potentiometer, the voltage difference is used to determine the position of the wiper along the resistive element. This similarity in operation is what led to potentiometers being referred to as pH meters.
| ROS-8600 RO Program Control HMI Platform | ||
| Model | ROS-8600 Single Stage | ROS-8600 Double Stage |
| Measuring range | Source water0~2000uS/cm | Source water0~2000uS/cm |
| First level effluent 0~200uS/cm | First level effluent 0~200uS/cm | |
| secondary effluent 0~20uS/cm | secondary effluent 0~20uS/cm | |
| Pressure sensor(optional) | Membrane pre/post pressure | Primary/ secondary membrane front/rear pressure |
| ph sensor(optional) | —- | 0~14.00pH |
| Signal collection | 1.Raw water low pressure | 1.Raw water low pressure |
| 2.Primary booster pump inlet low pressure | 2.Primary booster pump inlet low pressure | |
| 3.Primary booster pump outlet high pressure | 3.Primary booster pump outlet high pressure | |
| 4.High liquid level of Level 1 tank | 4.High liquid level of Level 1 tank | |
| 5.Low liquid level of Level 1 tank | 5.Low liquid level of Level 1 tank | |
| 6.Preprocessing signal | 6.2nd booster pump outlet high pressure | |
| 7.Input standby ports x2 | 7.High liquid level of Level 2 tank | |
| 8.Low liquid level of Level 2 tank | ||
| 9.Preprocessing signal | ||
| 10.Input standby ports x2 | ||
| Output control | 1.Water inlet valve | 1.Water inlet valve |
| 2.Source water pump | 2.Source water pump | |
| 3.Primary booster pump | 3.Primary booster pump | |
| 4.Primary flush valve | 4.Primary flush valve | |
| 5.Primary dosing pump | 5.Primary dosing pump | |
| 6.Primary water over standard discharge valve | 6.Primary water over standard discharge valve | |
| 7.Alarm output node | 7.Secondary booster pump | |
| 8.Manual standby pump | 8.Secondary flush valve | |
| 9.Secondary dosing pump | 9.Secondary dosing pump | |
| Output standby port x2 | 10.Secondary water over standard discharge valve | |
| 11.Alarm output node | ||
| 12.Manual standby pump | ||
| Output standby port x2 | ||
| The main function | 1.Correction of electrode constant | 1.Correction of electrode constant |
| 2.Overrun alarm setting | 2.Overrun alarm setting | |
| 3.All working mode time can be set | 3.All working mode time can be set | |
| 4.High and low pressure flushing mode setting | 4.High and low pressure flushing mode setting | |
| 5.The low pressure pump is opened when preprocessing | 5.The low pressure pump is opened when preprocessing | |
| 6.Manual/automatic can be chosen when boot up | 6.Manual/automatic can be chosen when boot up | |
| 7.Manual debugging mode | 7.Manual debugging mode | |
| 8.Alarm if communication interruption | 8.Alarm if communication interruption | |
| 9. Urging payment settings | 9. Urging payment settings | |
| 10. Company name,website can be customized | 10. Company name,website can be customized | |
| Power supply | DC24V±10% | DC24V±10% |
| Expansion interface | 1.Reserved relay output | 1.Reserved relay output |
| 2.RS485 communication | 2.RS485 communication | |
| 3.Reserved IO port, analog module | 3.Reserved IO port, analog module | |
| 4.Mobile/computer/touch screen synchronous display | 4.Mobile/computer/touch screen synchronous display | |
| Relative humidity | ≦85% | ≤85% |
| Environment temperature | 0~50℃ | 0~50℃ |
| Touch screen size | 163x226x80mm (H x W x D) | 163x226x80mm (H x W x D) |
| Hole Size | 7 inch:215*152mm(wide*high) | 215*152mm(wide*high) |
| Controller size | 180*99(long*wide) | 180*99(long*wide) |
| Transmitter size | 92*125(long*wide) | 92*125(long*wide) |
| Installation method | Touch screen:panel embedded; Controller: plane fixed | Touch screen:panel embedded; Controller: plane fixed |
One of the key advantages of using a potentiometer as a ph meter is its versatility. Potentiometers can be easily calibrated to measure pH levels accurately, making them a cost-effective alternative to traditional pH meters. Additionally, potentiometers are more durable and require less maintenance compared to pH meters, making them ideal for long-term use in various applications.
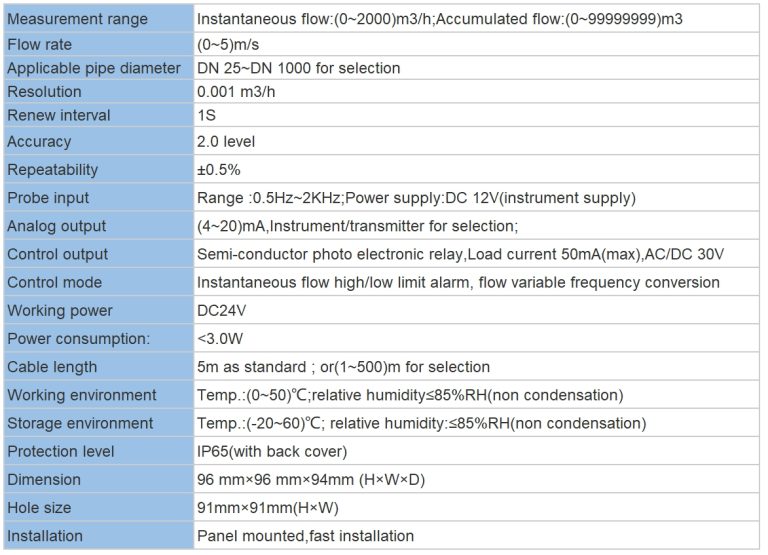
| FL-9900 High Precision Type Runner Flow Controller | ||
| Measuring range | Frequency | 0~2K Hz |
| Velocity of flow | 0.5~5 m/s | |
| Instantaneous flow | 0~2000 m³/h | |
| Cumulative flow | 0~9999 9999.999 m³ | |
| Applicable pipe diameter range | DN15~DN100;DN125~DN300 | |
| Resolution | 0.01 m³/h | |
| Refresh rate | 1s | |
| Accuracy class | Level 2.0 | |
| Repeatability | ±0.5% | |
| Sensor input | Radius:0~2K Hz | |
| Supply voltage:DC 24V(instrument internal supply) | ||
| The electronic unit automatically temperature compensates for errors | +0.5%FS; | |
| 4-20mA | Technical characteristics | Meter/transmitter dual mode (photoelectric isolation) |
| Loop resistance | 500Q(max),DC24V; | |
| Transmission accuracy | ±0.01mA | |
| Control port | Contact mode | Passive relay control output |
| Load capacity | Load current 5A (max) | |
| Function selection | Instantaneous flow upper/lower alarm | |
| Mains supply | Working voltage: DC24V 4V Power consumption :<; 3.OW | |
| Cable length | Factory configuration: 5m, can be agreed: (1~500) m | |
| Environmental requirement | Temperature: 0~50℃; Relative humidity: ≤85%RH | |
| Storage environment | Temperature: (-20~60) ℃; Humidity: 85%RH | |
| Overall dimension | 96×96×72mm(height × width × depth) | |
| Opening size | 92×92mm | |
| Installation mode | Disc mounted, fast fixed | |
| Sensor | Body material | Body: Engineering plastic PP; Bearing :Zr02 high temperature zirconia |
| Flow rate range | 0.5~5 m/s | |
| Withstand pressure | ≤0.6MPa | |
| Supply voltage | lDC 24V | |
| Output pulse amplitude| | Vp≥8V | |
| Normal pipe diameter | DN15~DN100;DN125~DN600 | |
| Medium characteristic | Single-phase medium(0~60℃) | |
| Installation mode | Direct line insertion | |
Another reason why potentiometers are also called pH meters is their ability to provide real-time measurements of pH levels. Unlike traditional pH meters that require calibration and adjustment, potentiometers can provide continuous monitoring of pH levels without the need for frequent recalibration. This makes potentiometers a valuable tool for researchers and scientists who need to monitor pH levels over an extended period of time.
In conclusion, the relationship between potentiometers and pH meters stems from their shared ability to measure voltage differences accurately. While potentiometers are traditionally used for measuring position or voltage in a circuit, they can also be calibrated to measure pH levels accurately, making them a versatile and cost-effective alternative to traditional pH meters. By understanding the similarities between these two devices, researchers and scientists can make informed decisions about which instrument is best suited for their specific needs.