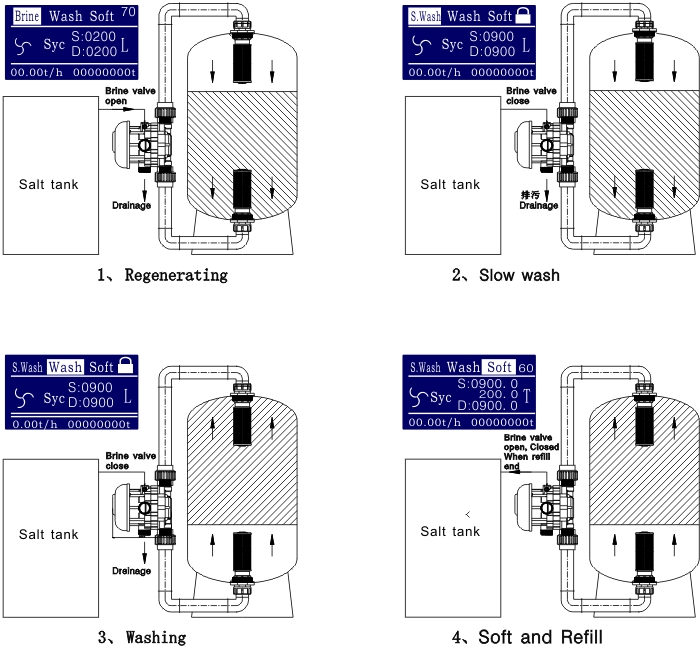
“Soft water, happy plants: the benefits of using a water softener in your garden.”
Effects of Water Softeners on Plant Health
Water softeners are commonly used in households to remove minerals such as calcium and magnesium from water, which can cause limescale buildup in pipes and appliances. While water softeners are beneficial for improving the quality of water for human use, there is some debate about their impact on plant health.
One of the main concerns with using water softened by a water softener on plants is the high levels of sodium that can be present. Sodium is not a nutrient that plants need in large quantities, and excessive levels can be harmful to plant health. When plants are watered with softened water containing high levels of sodium, the soil can become saline, leading to poor plant growth and even death in extreme cases.
In addition to sodium, water softened by a water softener may also contain elevated levels of chloride. Chloride is another element that can be harmful to plants in high concentrations. It can interfere with the uptake of essential nutrients by plants, leading to nutrient deficiencies and stunted growth.
Another issue with using water softened by a water softener on plants is the lack of beneficial minerals that are removed during the softening process. Calcium and magnesium are essential nutrients for plant growth, and their absence in softened water can lead to deficiencies in plants. This can manifest as yellowing leaves, poor fruit development, and overall reduced plant vigor.

Despite these potential drawbacks, there are ways to mitigate the negative effects of using water softened by a water softener on plants. One option is to dilute the softened water with unsoftened water to reduce the sodium and chloride levels. This can help prevent soil salinity and nutrient imbalances in plants.
Another approach is to use alternative water sources for watering plants, such as rainwater or water from a well. These sources are naturally soft and do not require the use of a water softener, eliminating the risk of sodium and chloride buildup in the soil.
| Model | Valve Material | Inlet/Outlet | Continuous (0.1Mpa drop) | Peak (0.175Mpa drop) | Cv** | Maximum Backwash (0.175Mpa drop) | Distributor Pilot | Drain Line | Brine Line | Mounting Base | Height (from top of the tank) |
| CM39 | Unleaded brass | 3″ | 56.81m³/h | 73.86m³/h | 65 | 100gpm | 3″ | 2″(male) | 3/4″(male) | 6″-8UN or FLG | 15″ |
It is also important to monitor the health of plants regularly when using water softened by a water softener. Look for signs of nutrient deficiencies, such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth, and adjust watering practices accordingly. Adding organic matter to the soil can also help improve nutrient availability for plants.
In conclusion, while water softeners can be beneficial for improving water quality for human use, they may have negative effects on plant health due to high levels of sodium and chloride and the removal of essential minerals. By taking steps to mitigate these effects, such as diluting softened water or using alternative water sources, it is possible to minimize the impact on plants. Monitoring plant health and adjusting watering practices as needed can help ensure that plants thrive despite the use of water softened by a water softener.