pH changes with temperature due to the impact on the dissociation of water and the equilibrium of acid-base reactions.
The Relationship Between pH and Temperature: Explained
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, with a range from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is considered neutral, while values below 7 are acidic and values above 7 are alkaline. The pH of a solution can be influenced by various factors, including temperature. In this article, we will explore the relationship between pH and temperature and why pH changes with temperature.
When it comes to pH, temperature plays a crucial role in determining the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. As temperature increases, the pH of a solution can change due to the effect of temperature on the dissociation of ions in the solution. This phenomenon is known as the temperature dependence of pH.
One reason why pH changes with temperature is the effect of temperature on the dissociation of weak acids and bases. In a solution containing a weak acid, for example, an increase in temperature can lead to an increase in the dissociation of the acid molecules, resulting in a higher concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and a decrease in pH. Conversely, a decrease in temperature can lead to a decrease in the dissociation of the acid molecules, resulting in a lower concentration of hydrogen ions and an increase in pH.

Similarly, in a solution containing a weak base, an increase in temperature can lead to an increase in the dissociation of the base molecules, resulting in a higher concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) and an increase in pH. On the other hand, a decrease in temperature can lead to a decrease in the dissociation of the base molecules, resulting in a lower concentration of hydroxide ions and a decrease in pH.

Another reason why pH changes with temperature is the effect of temperature on the ionic product of water. The ionic product of water, Kw, is a constant value at a given temperature. However, as temperature changes, the value of Kw also changes, leading to a change in the concentration of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions in the solution, and consequently, a change in pH.
Furthermore, the effect of temperature on the solubility of gases in water can also influence the pH of a solution. As temperature increases, the solubility of gases in water decreases, leading to a decrease in the concentration of dissolved gases such as carbon dioxide. This can result in a decrease in the formation of carbonic acid, which is responsible for lowering the pH of the solution.
| Instrument model | FET-8920 | |
| Measurement range | Instantaneous flow | (0~2000)m3/h |
| Accumulative flow | (0~99999999)m3 | |
| Flow rate | (0.5~5)m/s | |
| Resolution | 0.001m3/h | |
| Accuracy level | Less than 2.5% RS or 0.025m/s.whichever is the largest | |
| Conductivity | >20μS/cm | |
| (4~20)mA output | Number of channels | Single channel |
| Technical features | Isolated,reversible,adjustable, meter/transmission dual mode | |
| Loop resistance | 400Ω(Max), DC 24V | |
| Transmission accuracy | ±0.1mA | |
| Control output | Number of channels | Single channel |
| Electrical contact | Semiconductor photoelectric relay | |
| Load capacity | 50mA(Max), DC 30V | |
| Control mode | Instantaneous amount upper/lower limit alarm | |
| Digital output | RS485(MODBUS protocol ),Impulse output1KHz | |
| Working power | Power supply | DC 9~28V |
| source | Power Consumption | ≤3.0W |
| Diameter | DN40~DN300(can be customized) | |
| Working environment | Temperature:(0~50) ℃; Relative humidity: ≤85%RH(none condensation) | |
| Storage environment | Temperature:(-20~60) ℃; Relative humidity: ≤85%RH(none condensation) | |
| Protection grade | IP65 | |
| Installation method | Insertion pipeline installation | |
In conclusion, the relationship between pH and temperature is a complex one, influenced by various factors such as the dissociation of weak acids and bases, the ionic product of water, and the solubility of gases in water. Understanding how pH changes with temperature is important in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. By considering the effects of temperature on pH, scientists can better interpret experimental results and make more accurate predictions about the behavior of solutions at different temperatures.
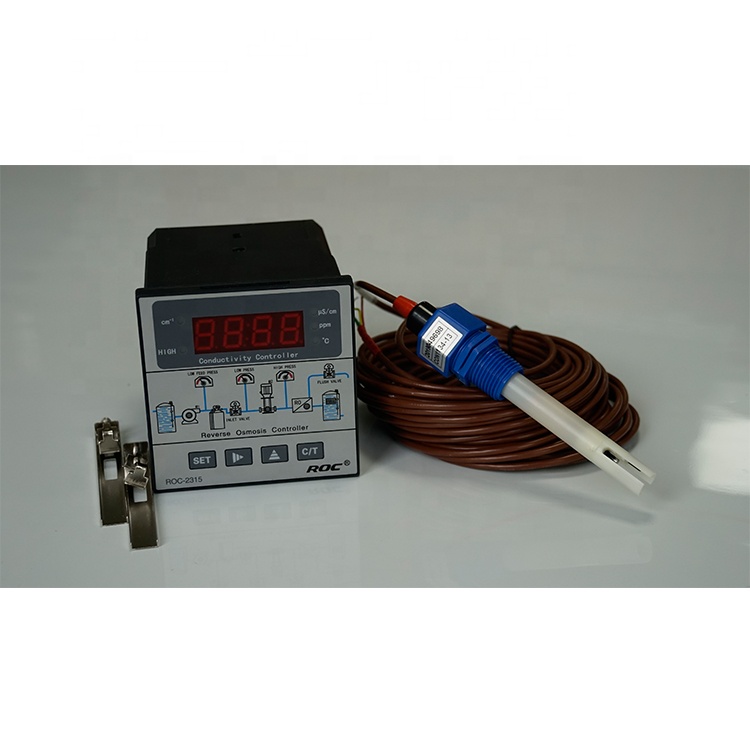
| ROC-2315 ro controller instruction (220V) | |||
| Model | ROC-2315 | ||
| Single detection | Dry Contact input | Raw water no water protection | |
| (six channels) | Low-pressure protection | ||
| High-pressure protection | |||
| Pure water tank high level | |||
| External control mode signal | |||
| Running reset | |||
| Control port | Dry Contact output | Raw water pump | SPST-NO low capacity : AC220V/3A Max ;AC110V/5A Max |
| (five channels) | Inlet valve | ||
| High pressure pump | |||
| Flush valve | |||
| Conductivity over-limit drainge valve | |||
| Measurement detection point | Product water conductivity and with Automatic Temperature compensation (0~50)℃ | ||
| Measurement range | Conductivity : 0.1~200μS/cm/1~2000μS/cm/10~999μS/cm (with different conductivity sensor ) | ||
| Product water temp. : 0~50℃ | |||
| Accuracy | 1.5 level | ||
| Power supply | AC220V (±10%) , 50/60Hz | ||
| Working environment | Temperature:(0~50)℃ ; | ||
| Relative Humidity :≤85%RH (no condensation ) | |||
| Dimension | 96×96×130mm( height ×width×depth) | ||
| Hole size | 91×91mm(height ×width) | ||
| Installation | Panel mounted ,fast installtion | ||
| Certification | CE | ||